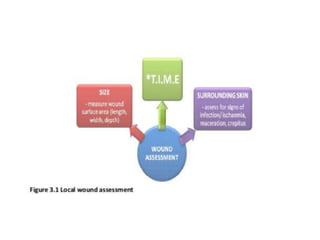
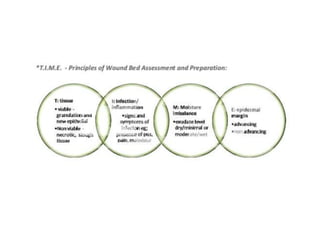
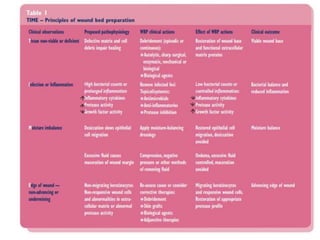
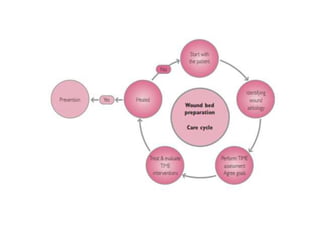
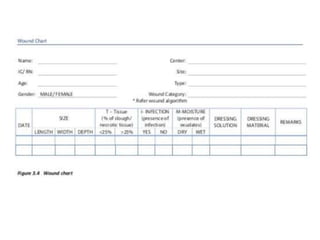
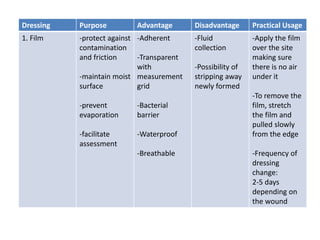
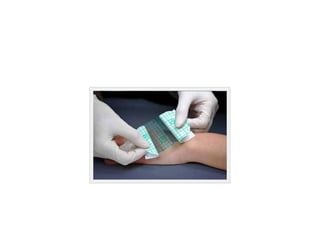
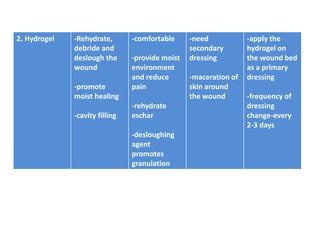
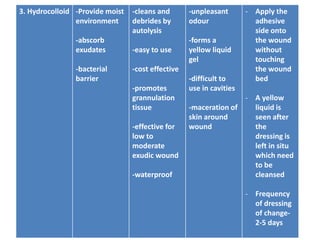
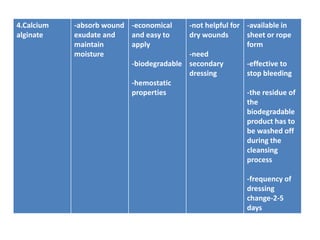
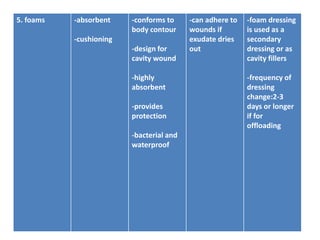
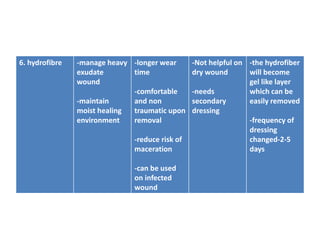
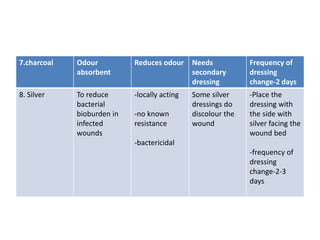
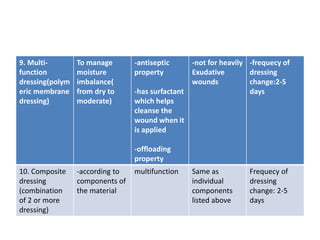
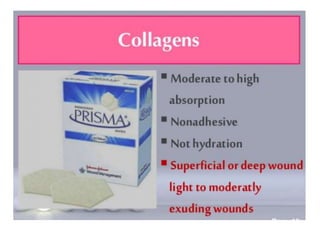
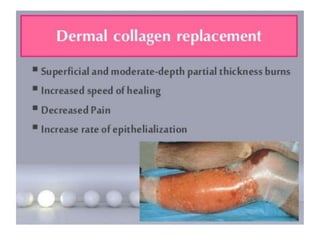
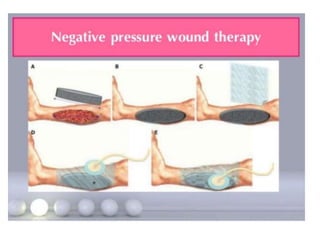
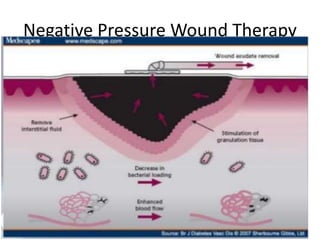
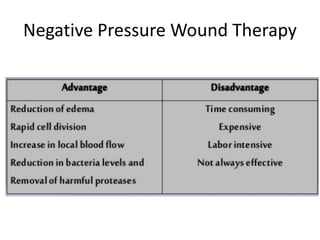
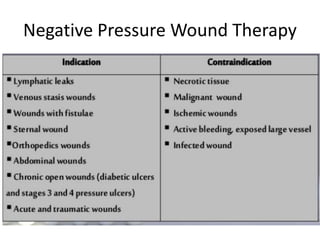
This document discusses wound assessment and modern wound dressings. It begins with an overview of general wound assessment, including identifying factors that may impede healing. Local wound assessment involves reviewing history and assessing characteristics like location, size and wound bed condition. Various modern dressings are then described, including films, hydrogels, hydrocolloids, calcium alginates and foams. Their purposes, advantages, disadvantages and usage are outlined. Negative pressure wound therapy is also summarized as a treatment for slow healing wounds using controlled subatmospheric pressure. Throughout, the document emphasizes proper wound cleaning and dressing selection based on wound type and condition.