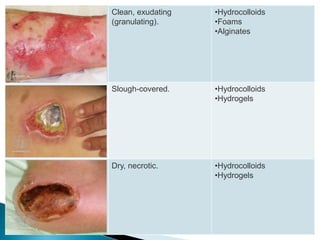
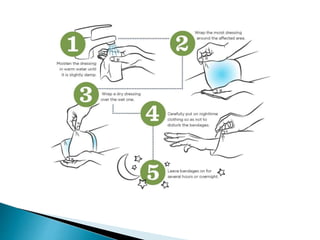
This document discusses wound dressings and their uses. It begins by defining wound dressings as sterile pads that promote healing and prevent harm. It then describes various types of dressings including gauze, hydrocolloids, hydrogels, films, alginates, and collagens. It provides details on their compositions, functions, and appropriate uses for different wound types. The document also covers topics like wound cleansing, wet wrap therapy, and potential dressing complications.