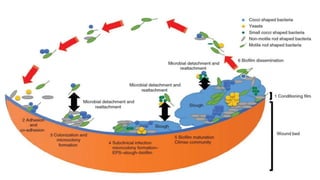
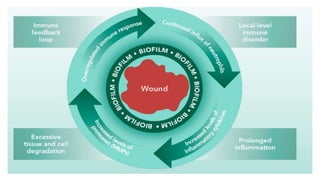
1. Wound debridement is the removal of dead, devitalized, contaminated, or foreign material from a wound to promote healing.
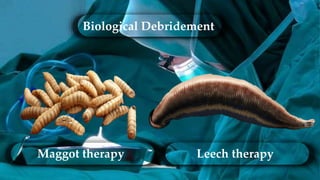
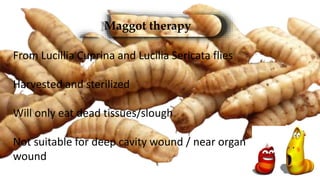
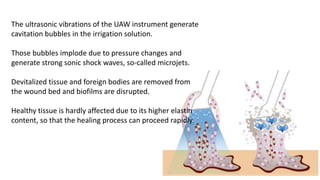
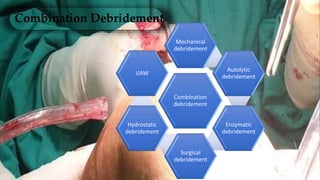
2. Various debridement methods are described, including mechanical, autolytic, enzymatic, surgical, hydrostatic, ultrasonic, and combinations of methods.
3. The appropriate debridement method depends on factors like the wound type, depth, and presence of infection or necrosis. The goal is to enhance healing by removing barriers and reducing bioburden.