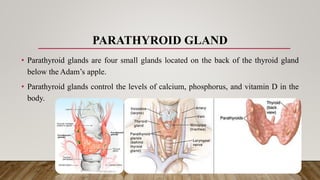
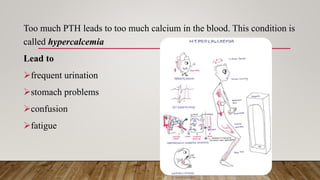
Primary hyperparathyroidism is caused by overproduction of parathyroid hormone by the parathyroid glands, located behind the thyroid gland. This excess hormone causes too much calcium in the blood, leading to symptoms like frequent urination, stomach problems, and fatigue. The condition is usually diagnosed through blood tests showing elevated parathyroid hormone and calcium levels. While tumors on the parathyroid glands are a common cause, enlarged glands can also lead to hyperparathyroidism. Surgery to remove the affected gland(s) is often the primary treatment.