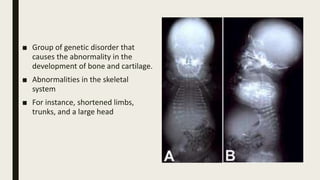
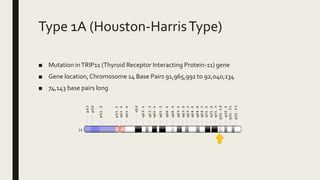
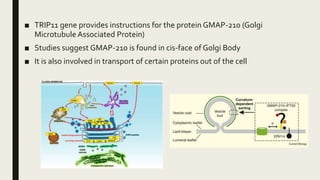
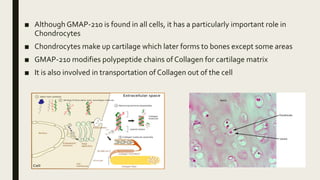
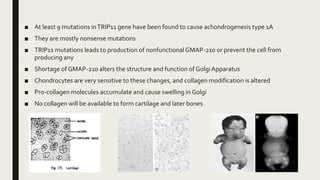
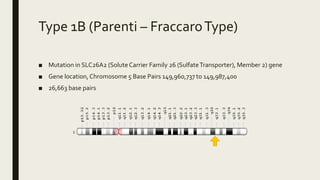
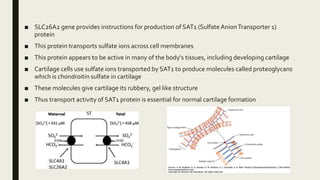
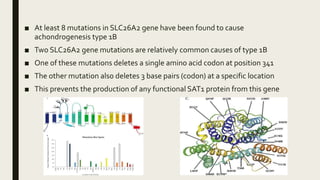
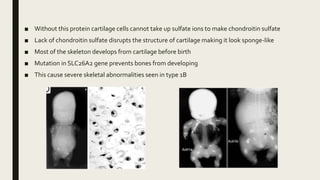
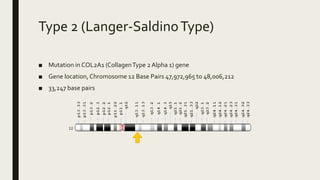
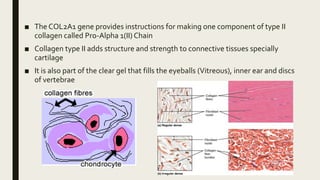
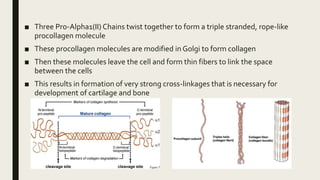
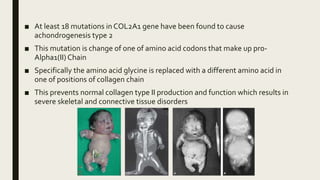
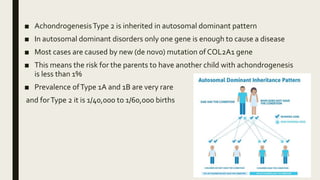
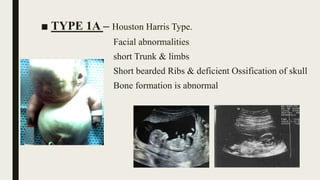
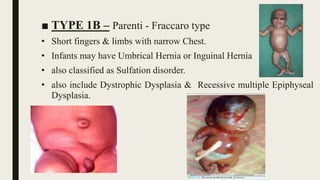
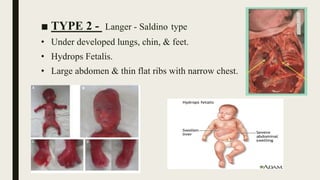
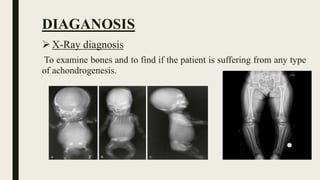
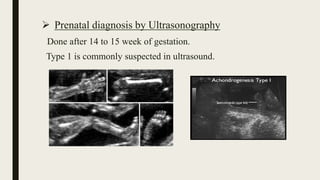
Achondrogenesis is a rare genetic disorder characterized by impaired bone and cartilage development. There are three main types caused by mutations affecting cartilage formation. Type 1A is caused by mutations impairing protein transport within cartilage cells. Type 1B results from mutations disrupting sulfate transport, critical for cartilage composition. Type 2 involves mutations altering collagen structure, fundamental to cartilage integrity. Affected infants exhibit severe skeletal abnormalities and often do not survive beyond infancy. Diagnosis involves x-rays and genetic testing. While incurable, treatment focuses on supportive care.