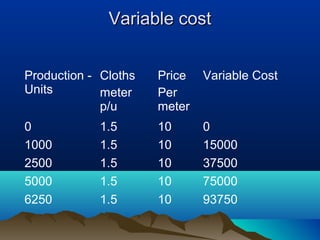
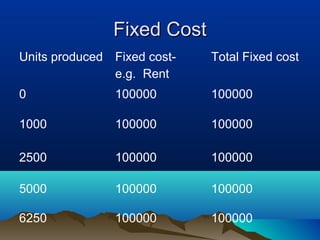
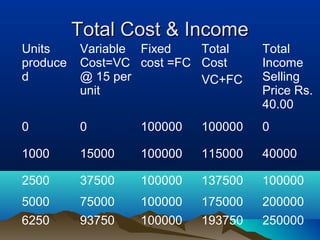
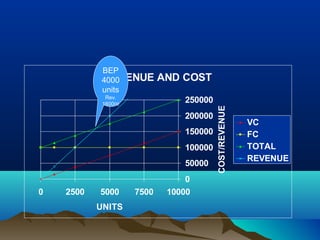
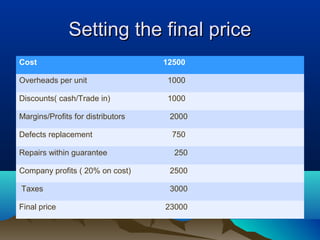
This document discusses pricing strategies and concepts. It covers the importance and objectives of pricing, factors to consider in pricing like costs and competitors, pricing strategies like cost-based, demand-based and competitor-based approaches. It also discusses concepts of costing for pricing like fixed costs, variable costs, contribution, break even point and margin pricing. The document provides examples and formulas to explain these pricing concepts.