1) Prevention aims to promote health and safety in communities by slowing the onset of disease through measures like health education, vaccinations, and early diagnosis.
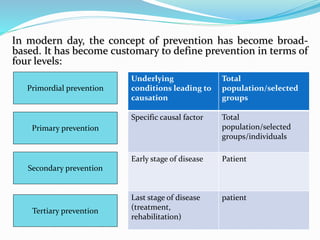
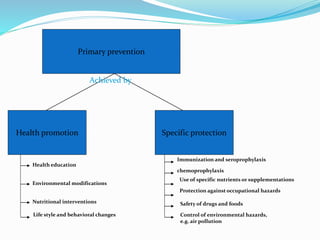
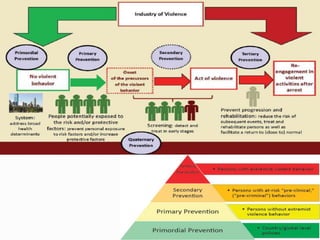
2) There are four levels of prevention: primordial focuses on whole populations, primary targets risk factors, secondary detects disease early, and tertiary manages existing conditions.
3) Successful prevention requires understanding disease causation and risk factors, implementing prophylactic measures for at-risk groups, and continuous evaluation of prevention programs. Going "upstream" to address root causes is most effective.







![Preventable Causes of Disease
BEINGS
Biological factors and Behavioral Factors
Environmental factors
Immunologic factors
Nutritional factors
Genetic factors
Services, Social factors, and Spiritual factors
[JF Jekel, Epidemiology, Biostatistics, and Preventive Medicine, 1996]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prevention-190325030119/85/Prevention-8-320.jpg)