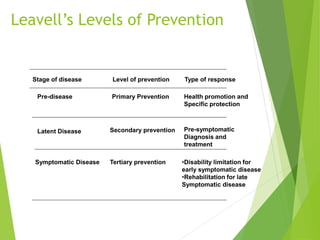
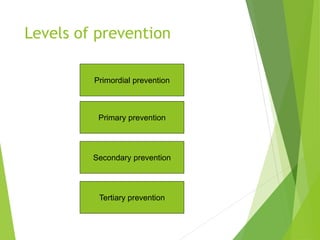
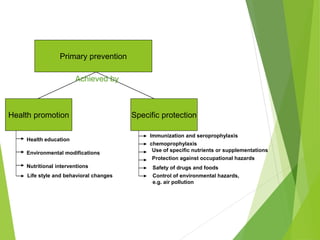
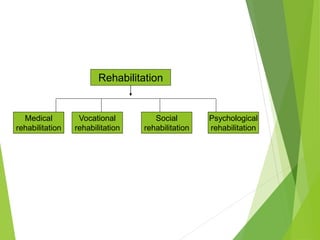
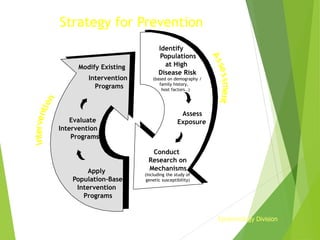
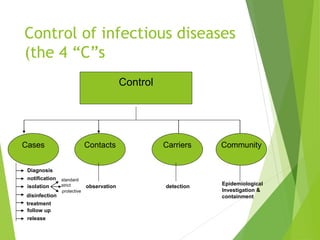
This document discusses concepts of disease prevention and control. It defines four levels of prevention: primordial, primary, secondary, and tertiary. Primordial prevention aims to prevent risk factors from emerging, while primary prevention removes the possibility of disease through measures like health promotion and immunization. Secondary prevention detects and treats disease early through screening to prevent complications. Tertiary prevention focuses on rehabilitation and reducing impairments for patients with advanced disease. Successful prevention depends on understanding disease causes and applying appropriate measures to at-risk groups. The goals of control are to reduce disease incidence, duration, transmission and effects on individuals and communities.





![Preventable Causes of Disease
BEINGS
Biological factors and Behavioral Factors
Environmental factors
Immunologic factors
Nutritional factors
Genetic factors
Services, Social factors, and Spiritual
factors
[JF Jekel, Epidemiology, Biostatistics, and Preventive Medicine, 1996]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/32311-230509092807-7120f50a/85/32311-ppt-6-320.jpg)