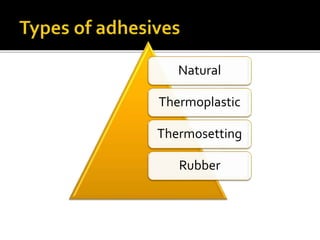
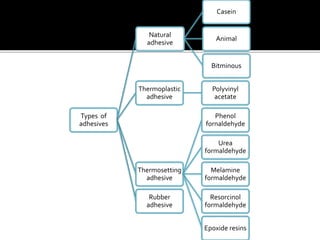
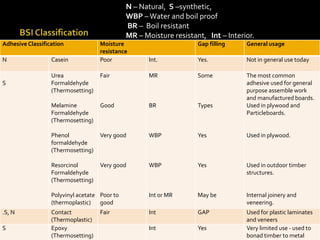
The document discusses different types of adhesives, including natural adhesives like casein glue and animal glue, thermoplastic adhesives like polyvinyl acetate, thermosetting adhesives such as phenol formaldehyde and epoxy resin, and rubber adhesives. It provides details on the composition and uses of these various adhesives and discusses British standard classifications for adhesives.