This document discusses different types of pressure measuring devices, including those that measure gauge pressure and absolute pressure. It describes several specific devices:
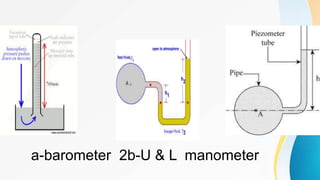
1) Barometers measure gauge pressure using a mercury-filled tube, with standard atmospheric pressure retaining the mercury at 760mmHg.
2) Manometers can be piezometers in an L-shape or U-shape, measuring the fluid height change in the tube relative to atmospheric pressure.
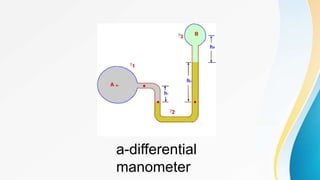
3) Differential manometers measure the absolute pressure difference between two connected fluid tanks, using the movement of a third reference fluid in the tube.