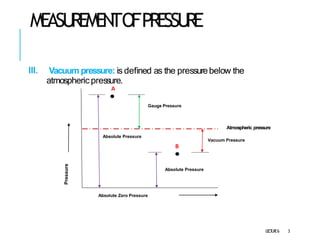
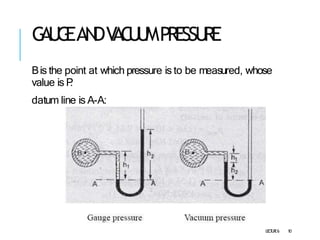
1. The document discusses various types of pressure measurement devices called manometers.
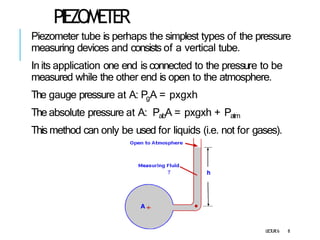
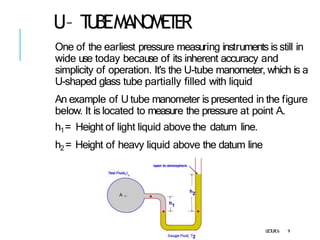
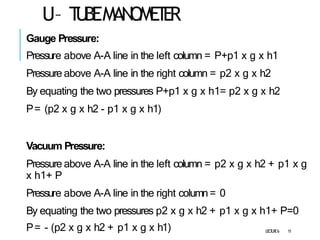
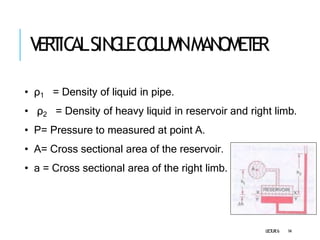
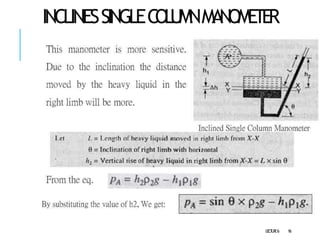
2. Manometers measure pressure using liquid columns and include simple manometers like piezometers and U-tube manometers, as well as differential manometers.
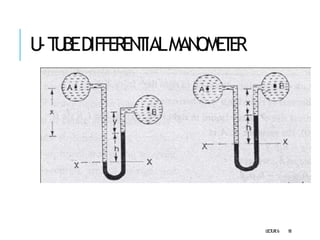
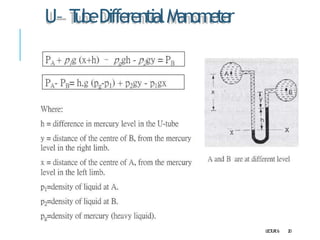
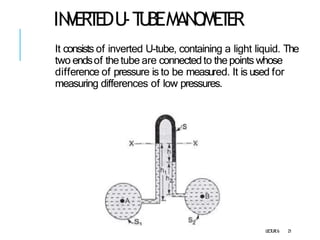
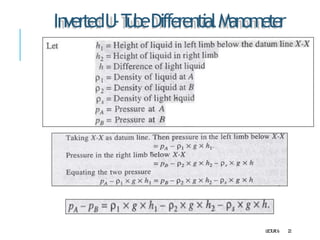
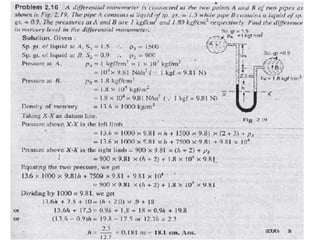
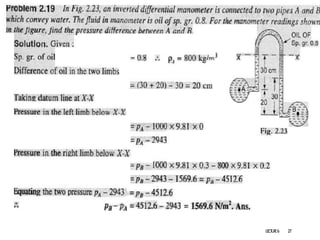
3. Differential manometers measure the difference in pressure between two points using a liquid-filled U-tube connected at both ends to the points of pressure.