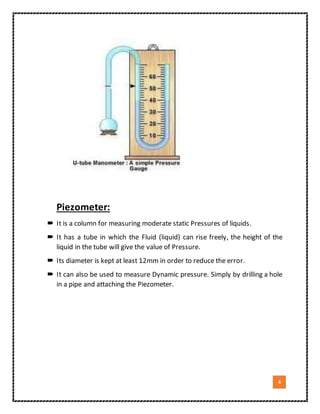
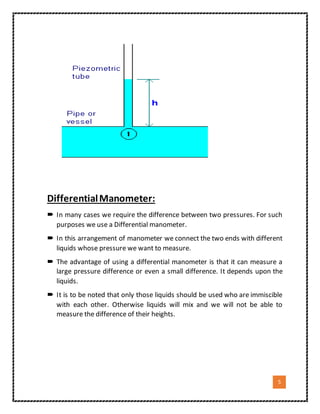
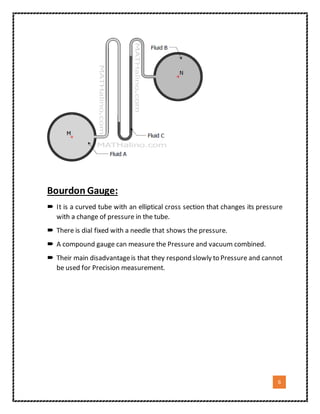
1. The document discusses different types of pressure measuring devices, including manometers, barometers, piezometers, differential manometers, and Bourdon gauges.
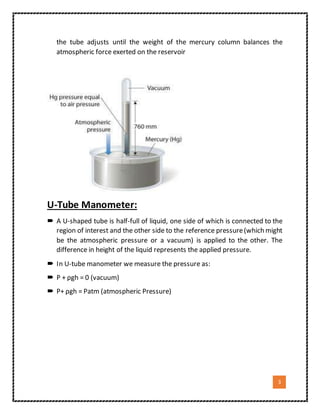
2. It explains how each device works, such as how a U-tube manometer uses the difference in height of two columns of liquid connected to areas of different pressures to measure the pressure difference.
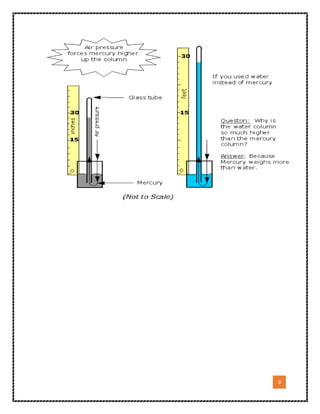
3. The document emphasizes that the type of liquid used in the device, called the gauge liquid, is important because liquids have different densities and properties that make some better suited for precise pressure measurement tasks. Mercury is often preferred for its high density and low vapor pressure.