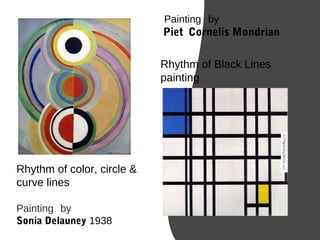
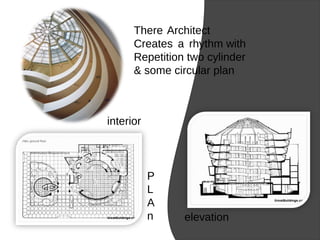
This presentation defines rhythm and discusses its role in architecture, music, painting, and nature. It begins by defining rhythm as a kind of repetition that occurs over time. Examples of natural rhythms include water waves and the human body. In music, rhythm is created through patterns of sounds and silences. In painting, the use of lines, shapes, colors and other elements can create visual rhythms, as shown in works by Mondrian and Delauney. The presentation then discusses how architects like Frank Lloyd Wright used rhythmic repetition of forms and shapes to create compositions in buildings such as the Guggenheim Museum and Taliesin West. It concludes that rhythm is a vital principle of design that allows for order, attention