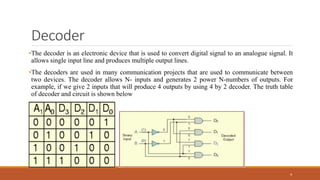
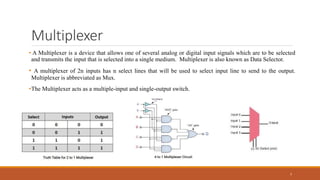
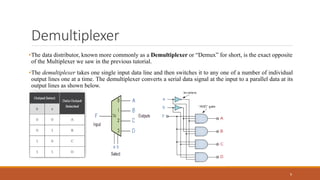
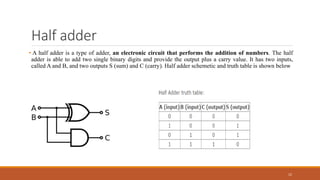
An encoder is a combinational circuit that performs the reverse operation of a decoder. It has up to 2N input lines and N output lines, and produces a binary code equivalent to the active input. A 4-to-2 encoder has four inputs and two outputs, where only one input can be '1' at a time to produce the respective binary code at the output. There are two main types of encoders: binary encoders and priority encoders. Decoders convert digital signals to analog signals and have N inputs and 2N outputs. Multiplexers have n select lines to choose one of several input signals to send to a single output, while demultiplexers take a single serial input and switch it to one