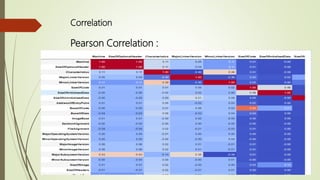
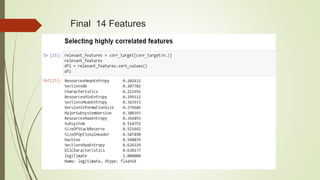
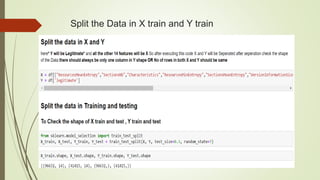
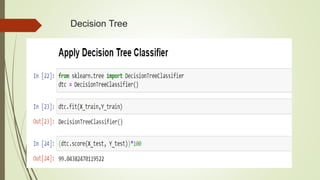
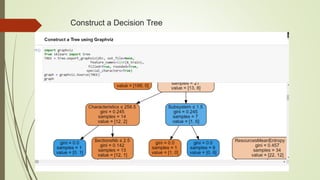
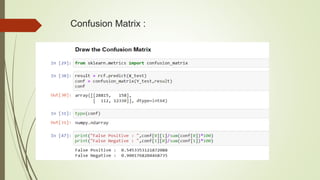
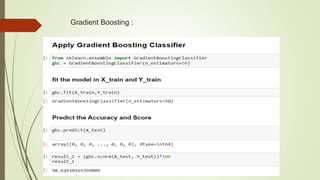
This document discusses using machine learning algorithms to detect malware files. It introduces different types of malware and provides an overview of machine learning methods for malware detection, including random forests, gradient boosting, and adaboost. The objectives are to use machine learning to detect legitimate and malware files and achieve high testing accuracy. The dataset includes over 130,000 files labeled as legitimate or malware. Several algorithms are applied including decision trees, random forests and gradient boosting. Random forests achieved the highest accuracy of 99.35% at distinguishing between legitimate and malware files.