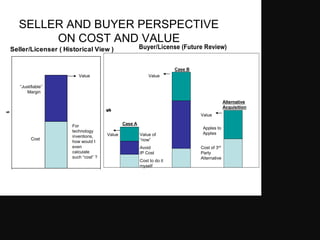
- The net present value of the business's projected cash flows over 5 years is RM230,000. To generate a 24% return, the purchase price today should be RM230,000.
- Discounting the annual cash flows back using a 24% discount rate, the net present value is RM230,000. This indicates the maximum purchase price to achieve the targeted 24% return.