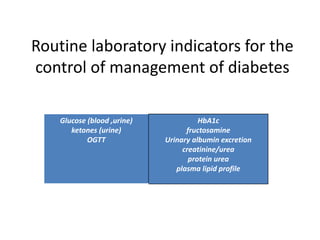
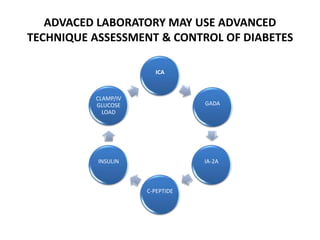
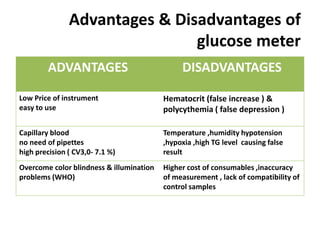
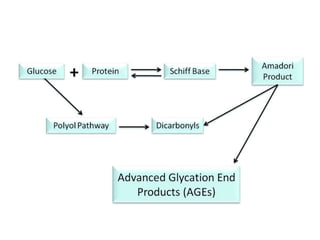
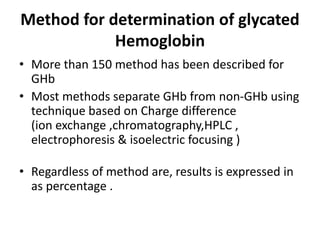
The document discusses the role of medical laboratories in managing diabetes mellitus. It outlines several routine laboratory indicators used to monitor diabetes, including glucose, HbA1c, lipids, and urinary albumin. Advanced tests like c-peptide and glucose clamps can also help assess diabetes. Laboratories play a key role in monitoring both acute issues like ketoacidosis and long-term control through markers like HbA1c. Self-monitoring of blood glucose is important for patients on insulin therapy. Reference ranges are provided for interpreting several diabetes-related laboratory tests.