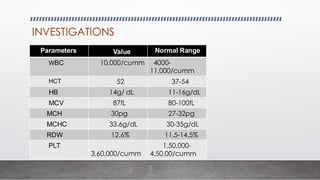
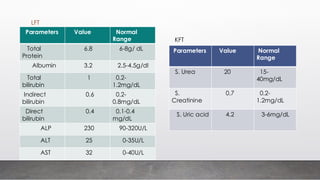
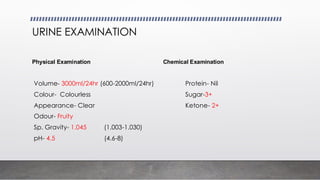
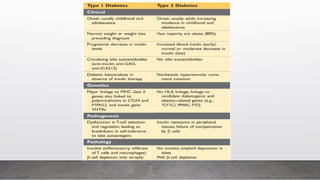
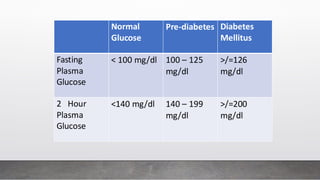
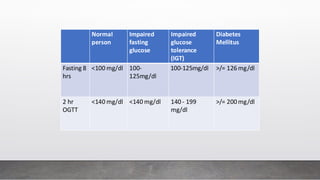
A 25-year-old male presented with symptoms including breathlessness, nausea, vomiting, weight loss, and increased urination, leading to a diagnosis of type 1 diabetes mellitus with diabetic ketoacidosis. Laboratory investigations revealed significantly elevated blood sugar levels and abnormal electrolyte balance. Various tests for diabetes diagnosis, monitoring, and complications were discussed, emphasizing the importance of plasma glucose estimation methods.