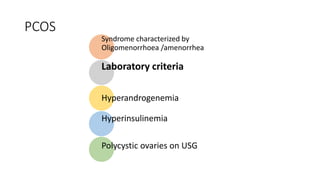
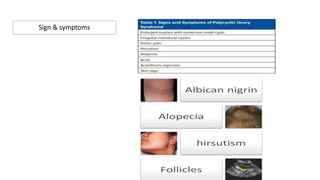
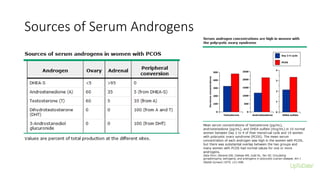
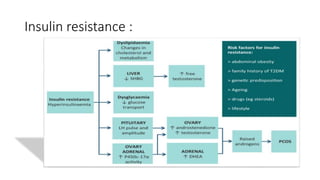
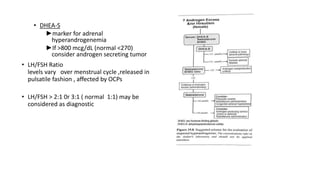
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is the most common endocrine abnormality and cause of infertility in women of reproductive age. PCOS is characterized by oligomenorrhea/amenorrhea, hyperandrogenism, and polycystic ovaries on ultrasound. The pathophysiology involves an altered hypothalamic-pituitary feedback loop leading to excessive LH production and androgen excess from the ovaries. Insulin resistance also contributes to hyperandrogenism and anovulation. Labs used to diagnose PCOS show increased androgens, LH levels relative to FSH, and markers of insulin resistance. Differential diagnoses must be ruled out through appropriate testing.