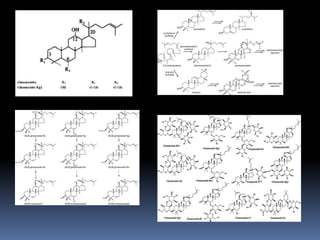
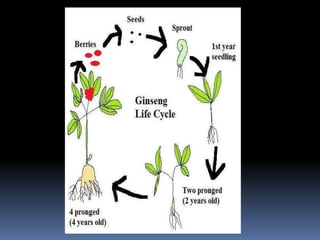
Ginseng is a perennial plant with fleshy roots belonging to the genus Panax. The two most common varieties are Asian ginseng (Panax ginseng) and American ginseng (Panax quinquefolius). Ginseng grows wild in northeast Asia and North America. It has been used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat various conditions like erectile dysfunction, cardiovascular issues, cancer, and weight control. The active compounds in ginseng include ginsenosides, polysaccharides, and fatty acids. Common side effects of ginseng include insomnia, diarrhea, and skin rashes if taken in excessive amounts.