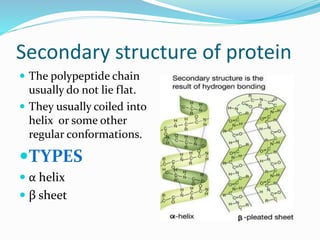
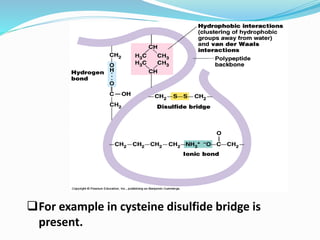
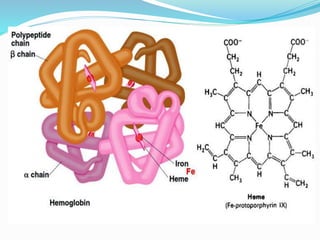
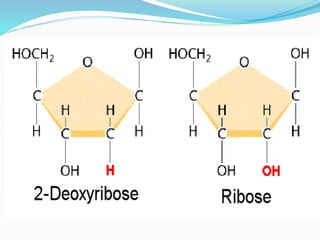
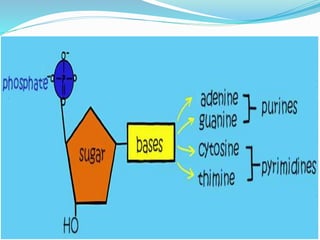
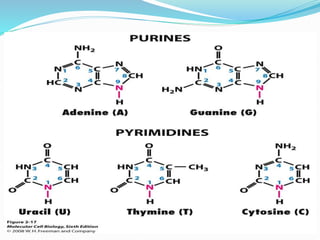
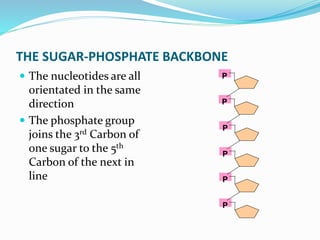
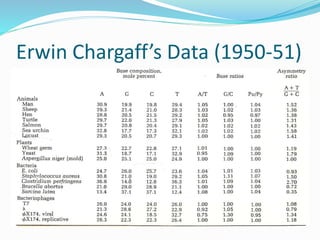
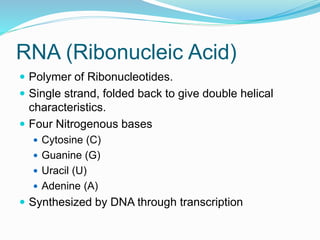
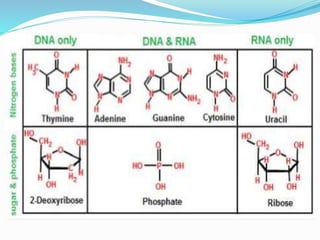
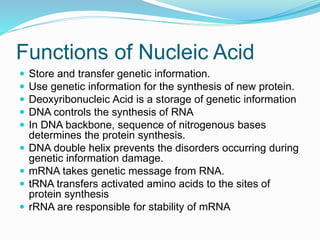
This document discusses the structure and functions of proteins and nucleic acids. It provides details on the primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure of proteins. It also describes the basic components and double helix structure of DNA and RNA. The key roles of DNA in storing genetic information and RNA in synthesizing proteins are summarized.