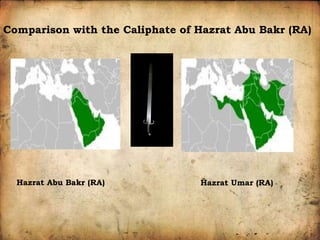
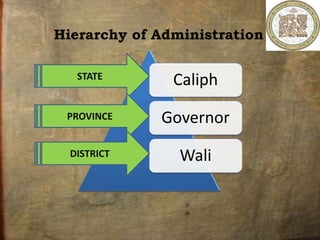
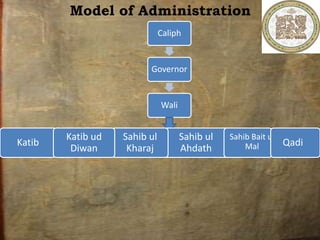
Hazrat Umar ibn Al-Khattab established an advanced administrative system during his reign as Caliph from 634 to 644 CE. He divided the Islamic empire into provinces, each led by a governor. Key departments included military, taxation, education, police, and financial. Umar introduced principles of accountability, separated government and private business, and established equal law for all. His reforms helped the rapidly expanding Muslim state address challenges like famine and wars with neighboring empires. Umar established foundations for efficient governance that helped strengthen and stabilize the early Muslim community.