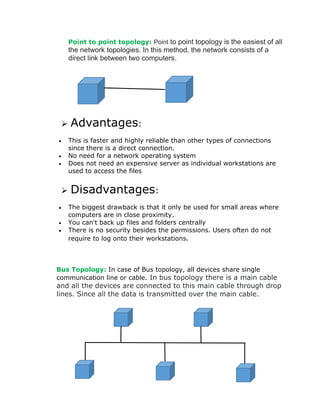
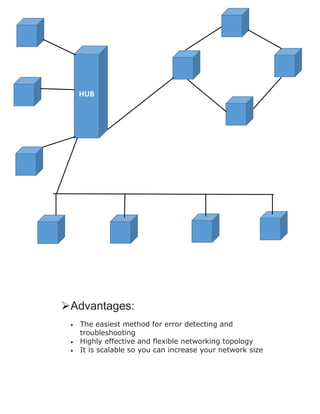
This document discusses different network topologies, including physical and logical topologies. It describes point-to-point, bus, ring, star, tree, mesh, and hybrid topologies. Each topology is defined along with its advantages and disadvantages. For example, the star topology connects all computers to a central hub, making it easy to set up and modify but if the hub fails the whole network fails. The mesh topology connects each device directly to every other device, providing redundancy but requiring many cables. A hybrid topology combines two or more standard topologies to achieve flexibility and scalability but with increased complexity.