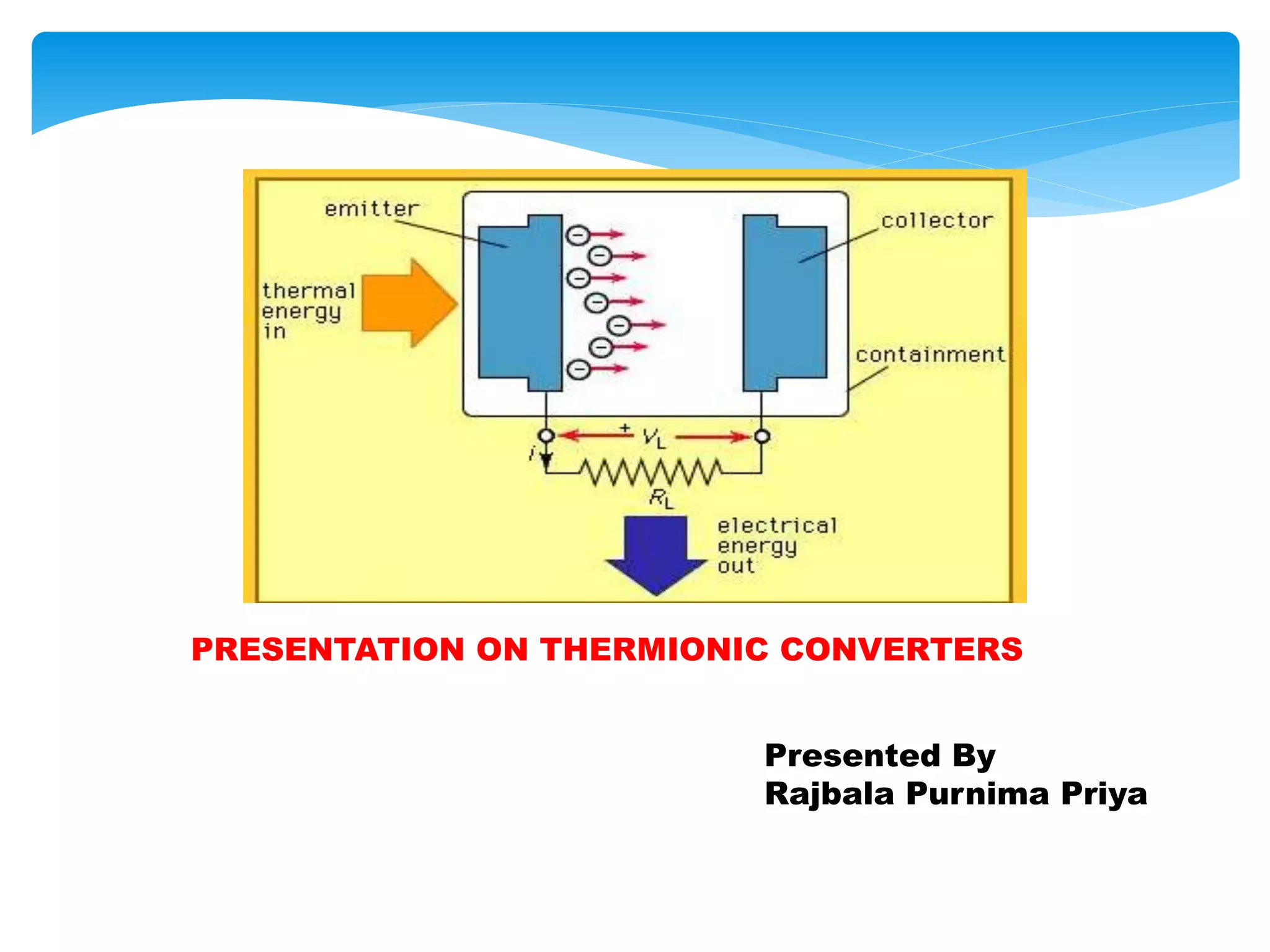
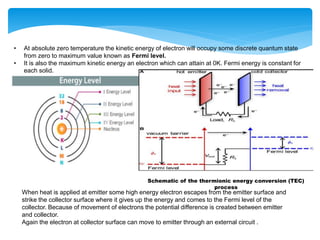
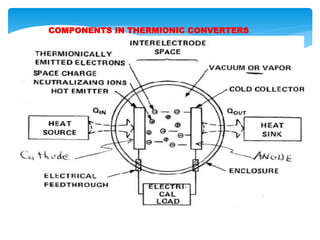
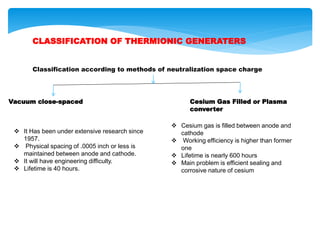
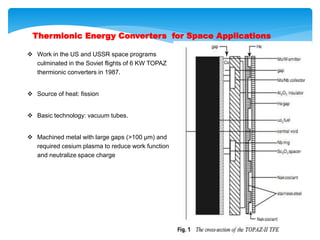
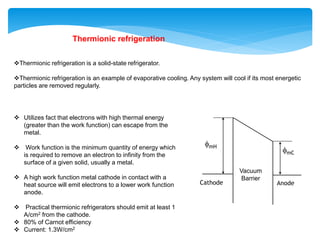
This document presents information on thermionic converters. It discusses their principle of operation, which involves heating an emitter surface to around 1800K so that electrons are emitted across a small gap to a cooler collector surface of around 1000K, creating a potential difference. The key components and typical operating conditions are described. Thermionic generators can be classified based on their method of neutralizing space charge. Advantages include having no rotating equipment, while disadvantages include low voltage output requiring many converters connected in series. Applications discussed include space power systems, solar thermionic hybrids, and solid-state refrigeration.