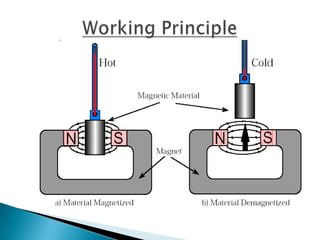
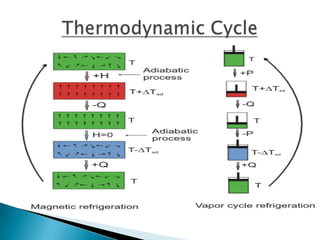
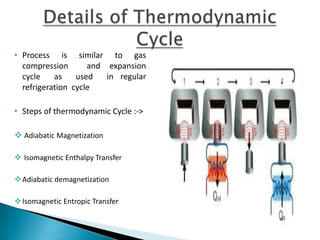
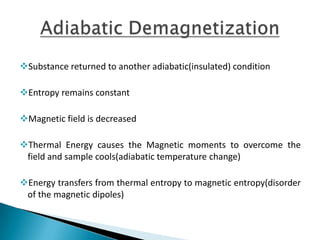
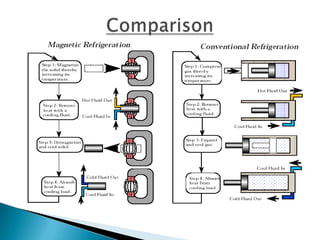
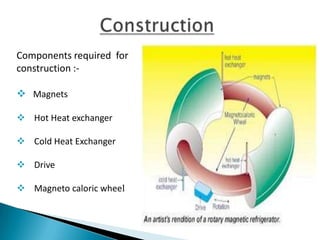
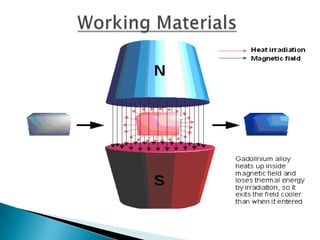
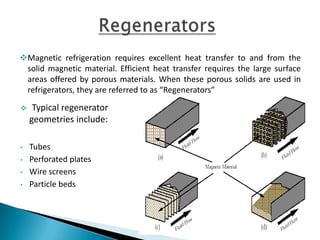
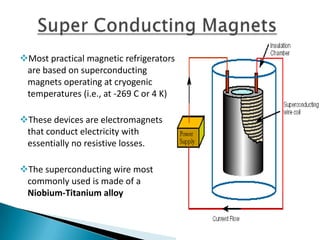
This document discusses magnetic refrigeration, which provides cooling through the magnetocaloric effect. It begins by introducing magnetic refrigeration and the magnetocaloric effect. It then covers the basic principles and mechanism of magnetic refrigeration, including the thermodynamic cycle and components required. Potential magnetocaloric materials are discussed. Applications for magnetic refrigeration include household appliances, buildings, transportation, food storage, and electronics cooling. Benefits include higher efficiency and lower environmental impact compared to traditional refrigeration. Further research is still needed to improve temperature changes and develop stronger permanent magnets for widespread commercial use.