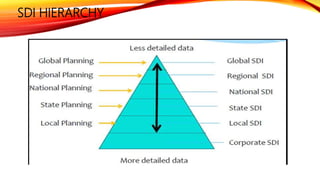
The document outlines the structure and functions of Nepal's national mapping organization and spatial data infrastructure (SDI), managed by the Survey Department under the Ministry of Land Management. It details the objectives and major activities of the National Geographic Information Infrastructure Division (NGIID) as well as the advantages and challenges of the SDI. The conclusion emphasizes the need for a standard national policy to enhance communication, cooperation, and the adoption of new technologies in the development of spatial data infrastructure.