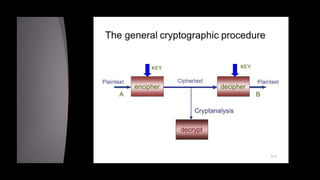
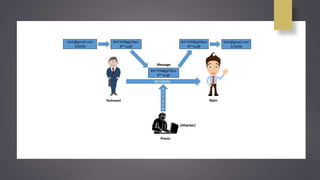
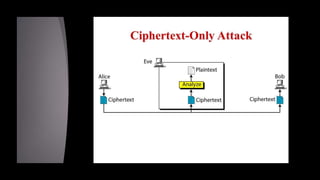
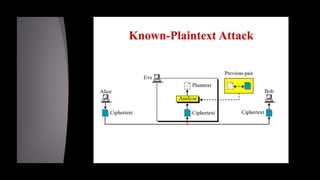
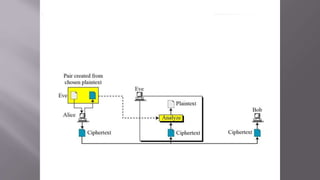
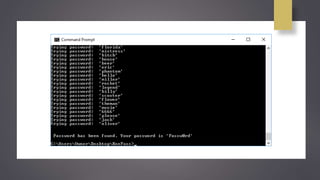
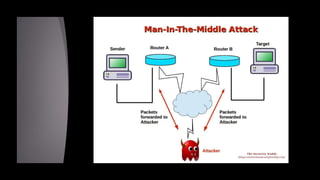
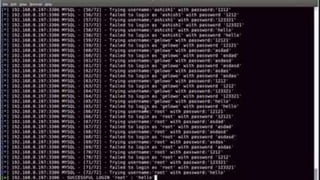
Cryptanalysis is the study of encrypted messages to understand encryption systems and find weaknesses. Cryptanalysts aim to decrypt messages without knowing the encryption key or algorithm. Their research helps cryptographers strengthen algorithms. Cryptanalysts uncover design flaws that can reduce the number of keys tested on a message. Their work is used by governments and companies to test security products.