I. The document discusses states of matter and phase changes. It includes questions and answers about solids, liquids, and gases.
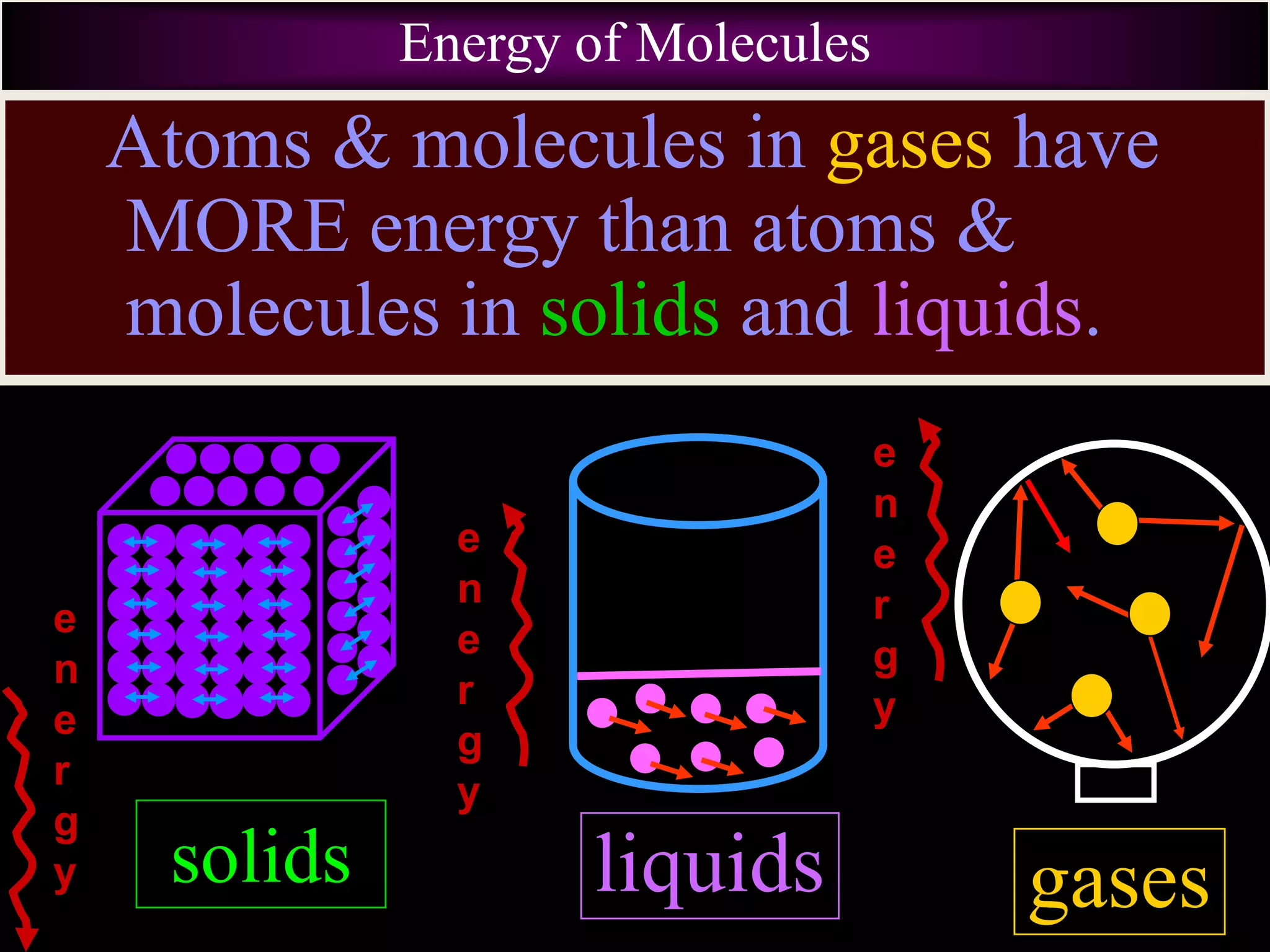
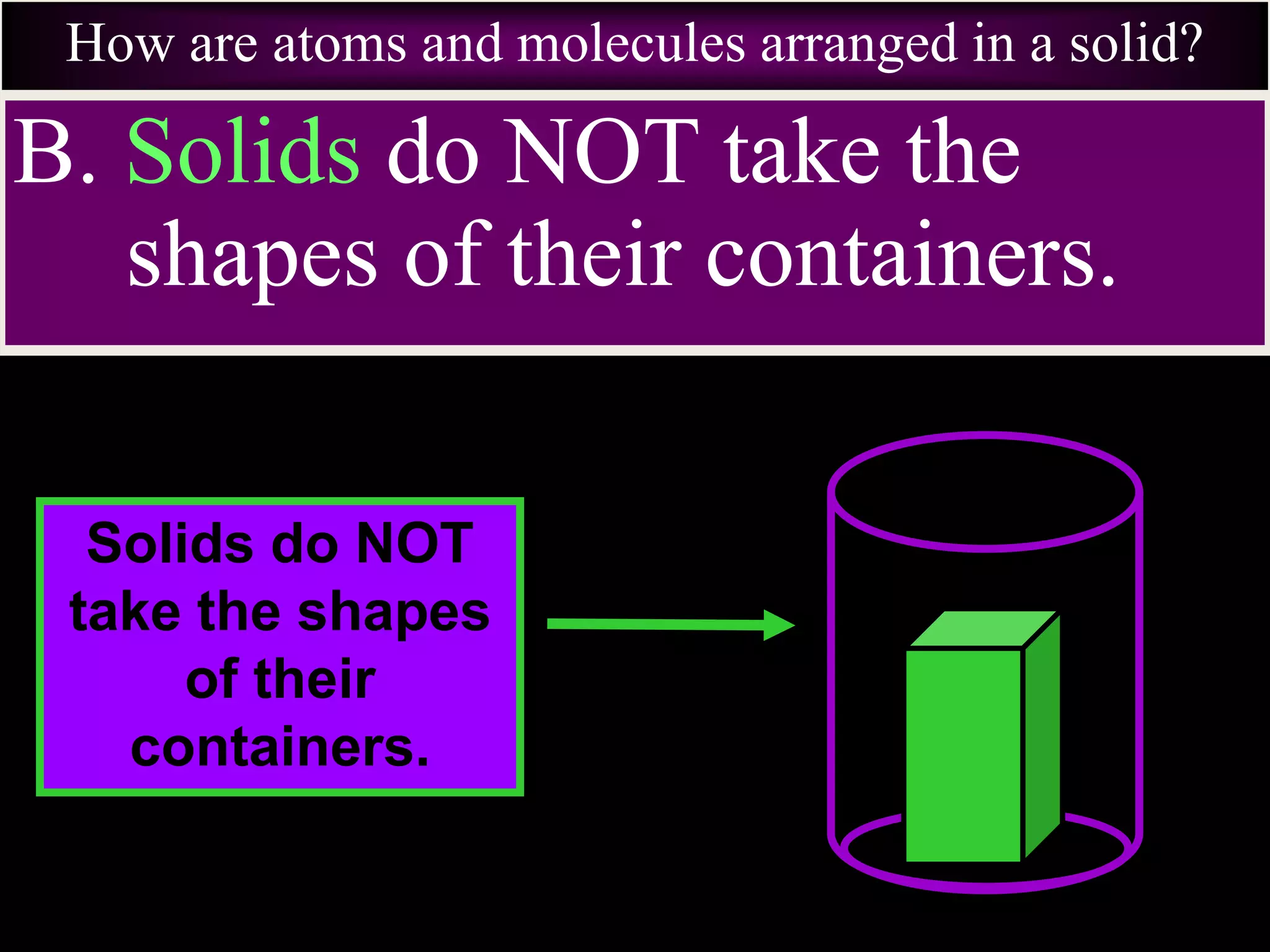
II. Solids have a definite shape and volume, liquids take the shape of their container but maintain a constant volume, and gases fill their container and have no definite shape or volume.
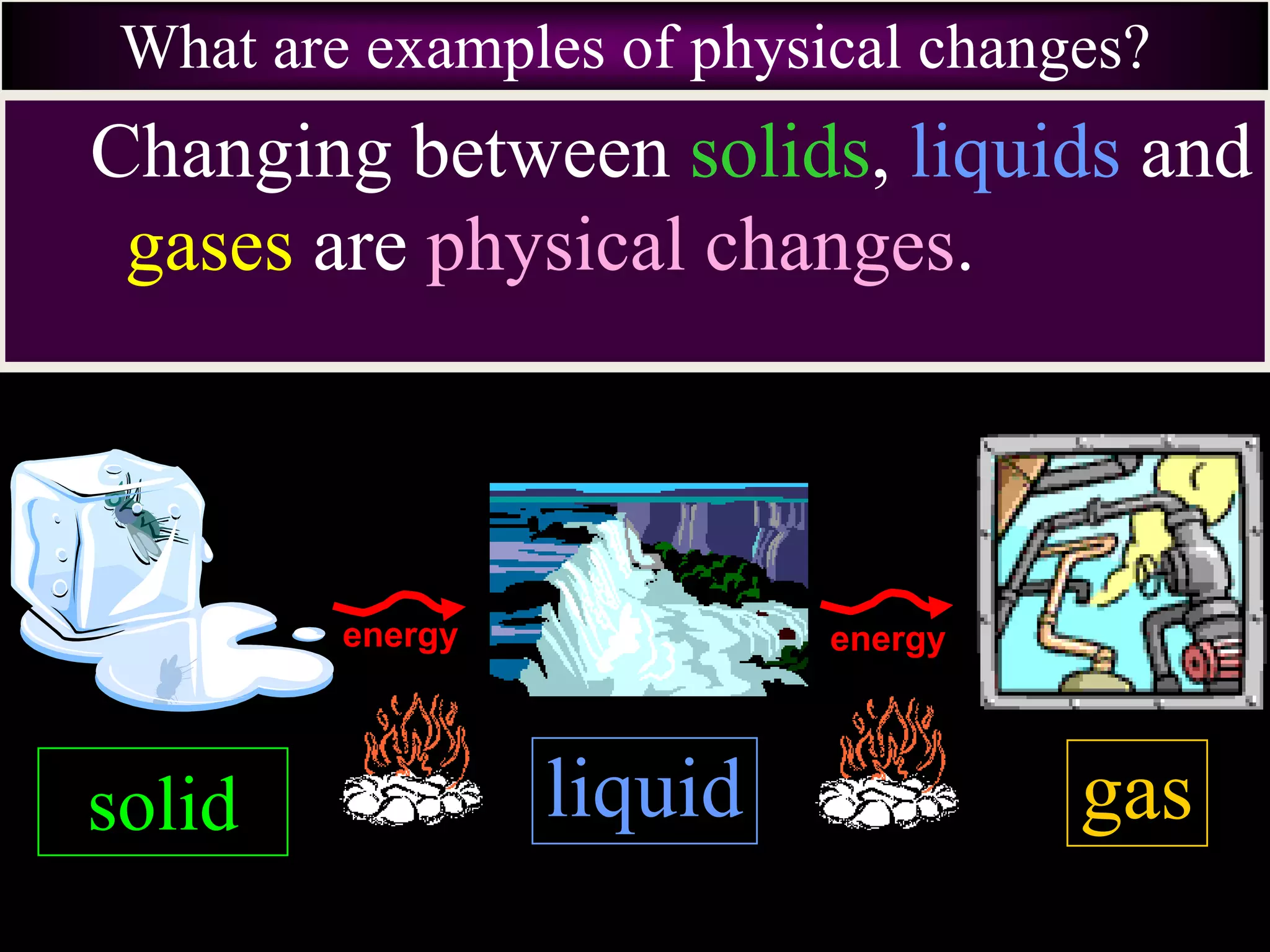
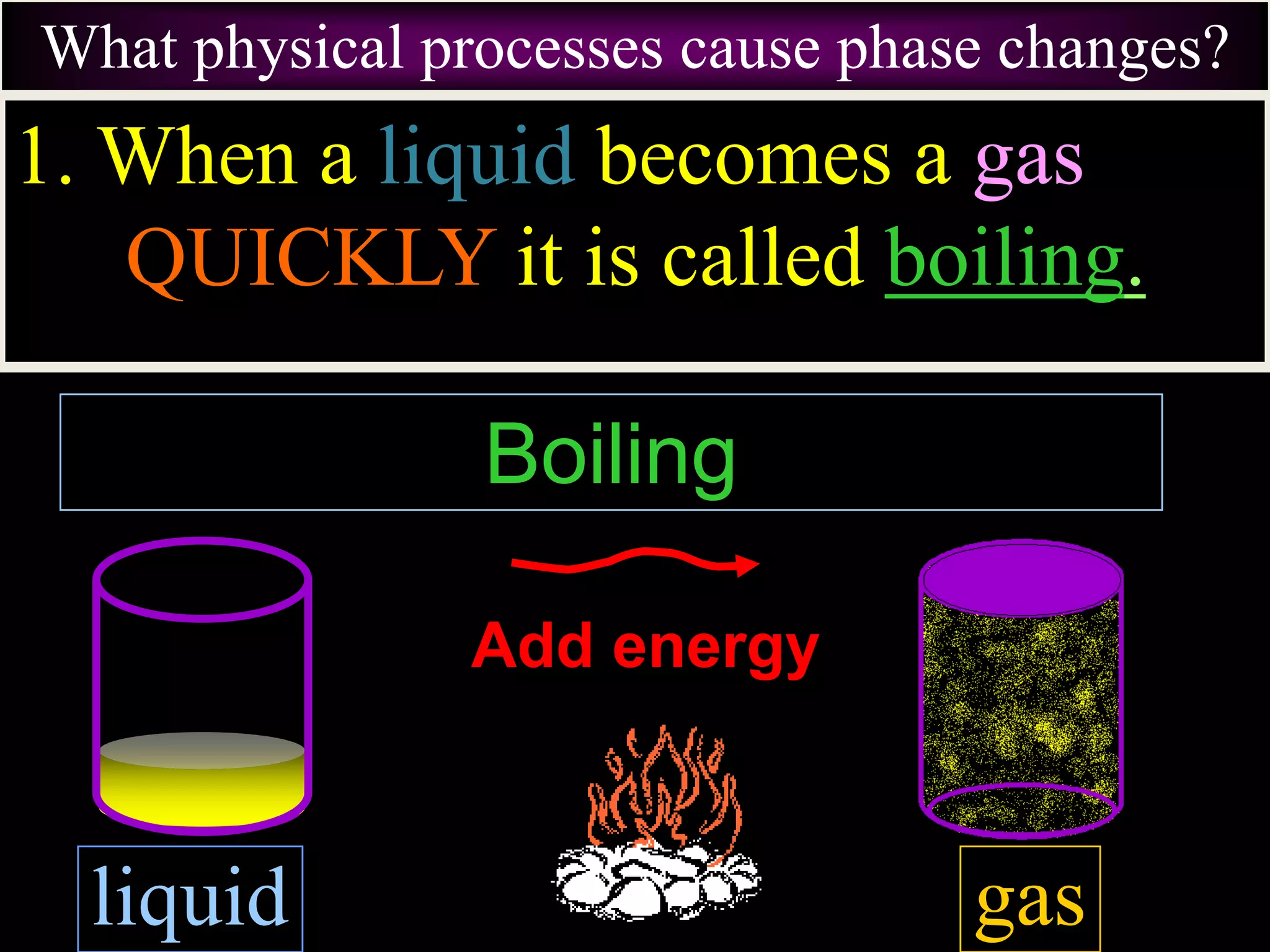
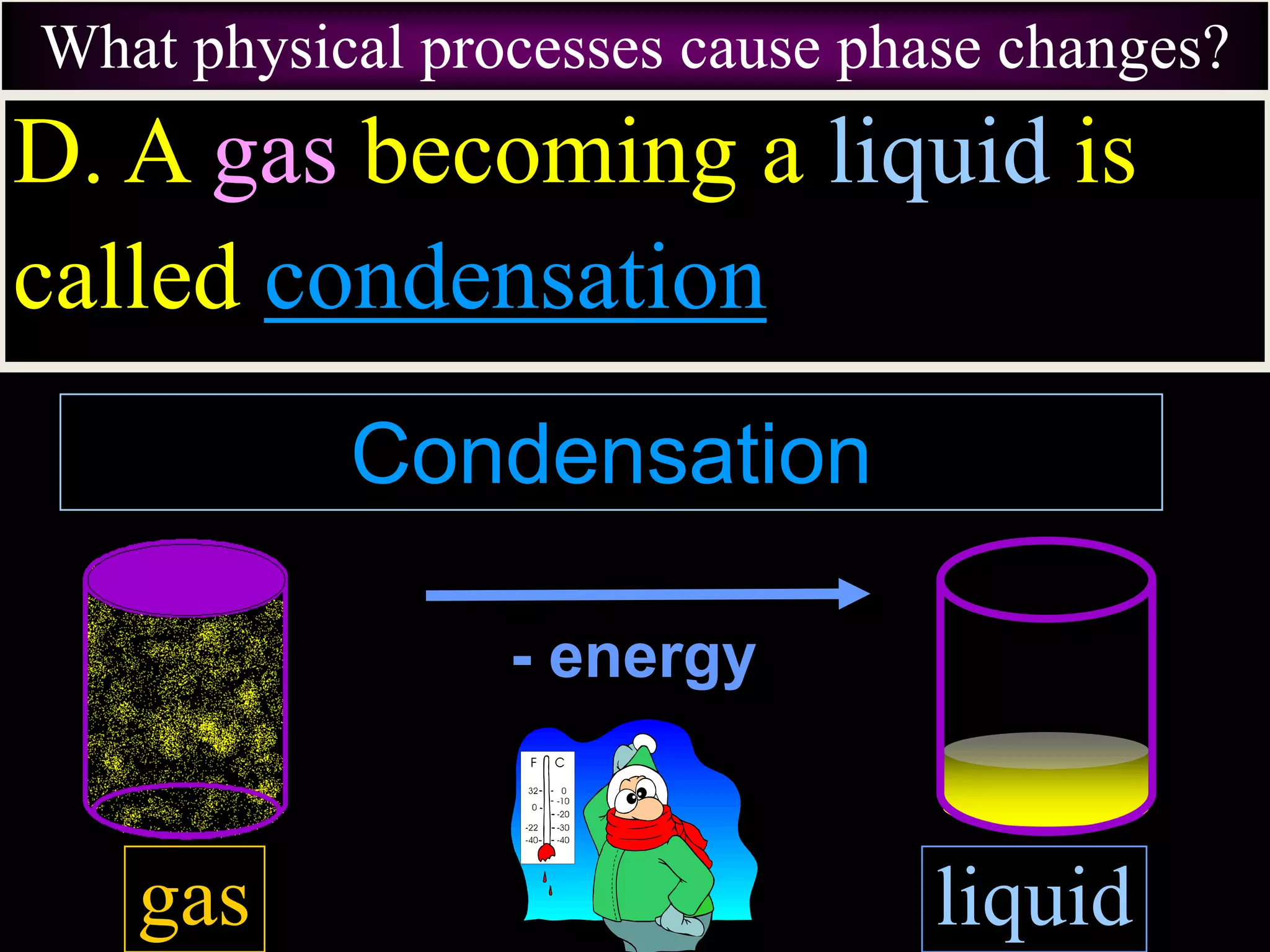
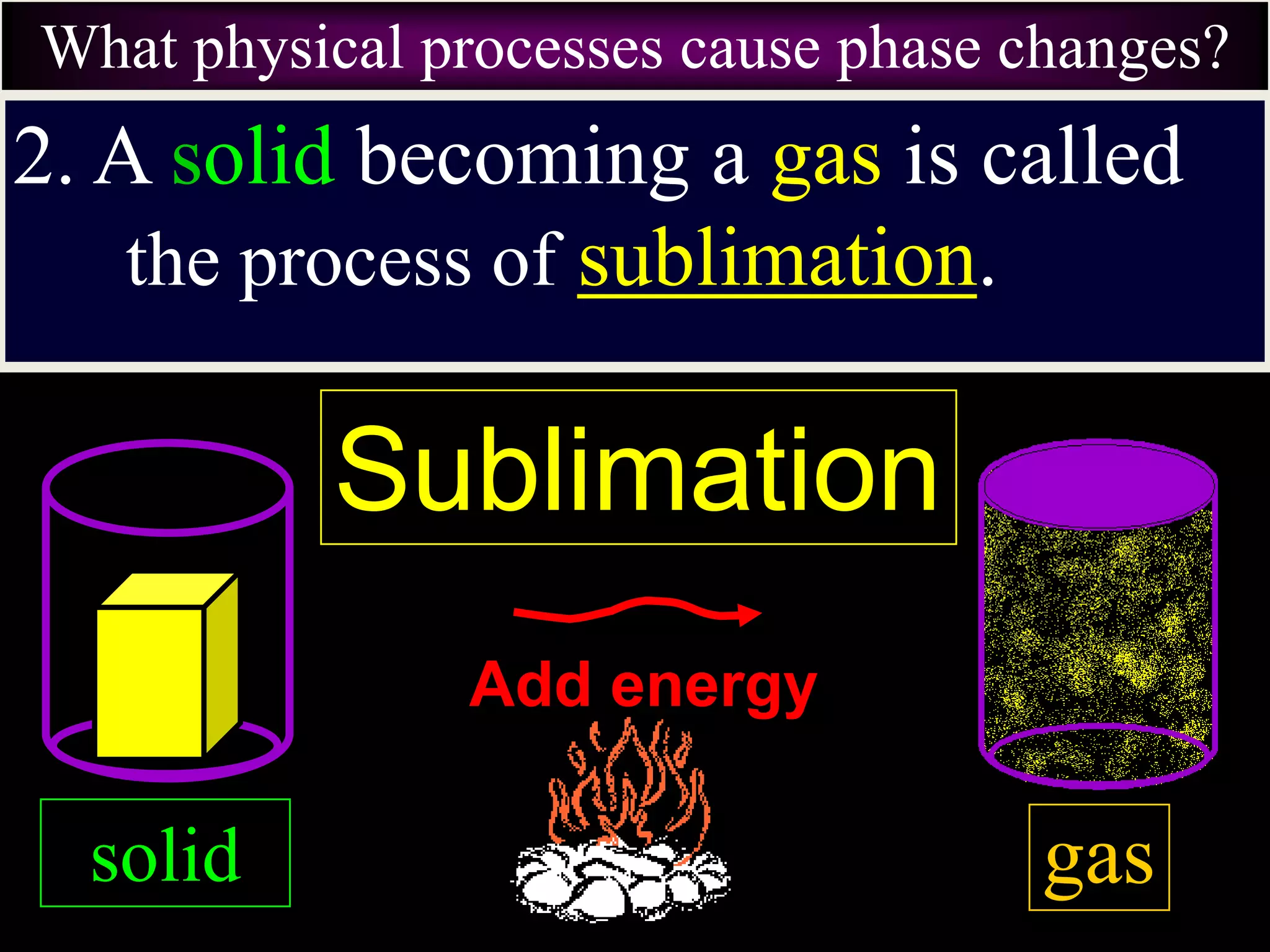
III. Phase changes between solids, liquids and gases are physical changes that do not create new substances; they involve the addition or removal of energy causing atoms and molecules to move faster or slower and be closer together or farther apart.