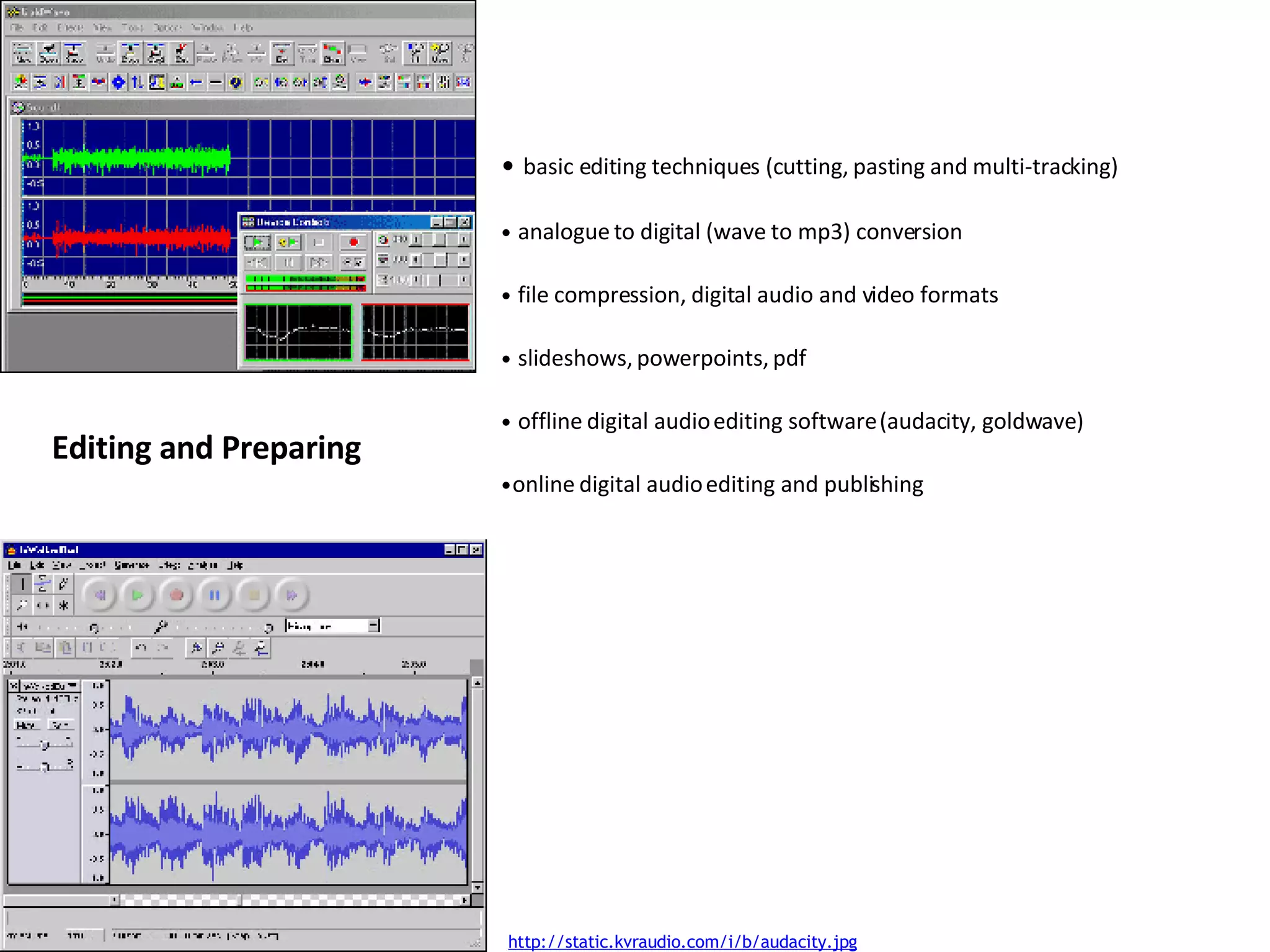
The document discusses creating and delivering digital audio courses in a flexible learning environment. It emphasizes enhancing learning through varied audio content and activities. Flexible design considerations include allowing flexibility in timing, content, and delivery methods to improve accessibility and cater to diverse learners. The document also addresses using open educational resources and collaborative projects to foster learning communities.
![DFLP 2008 CREATING DIGITAL AUDIO July 2008 Otago Polytechnic Dunedin [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-of-dflp-1218511760967179-8/75/Presentation-Of-Dflp-1-2048.jpg)