The document discusses several medical procedures and conditions:
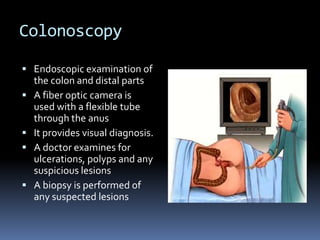
Colonoscopy involves using a camera to examine the colon for issues like polyps. Risks are low but include perforation. Screening is recommended starting at age 50.
Cholelithiasis refers to gallstones, which are crystalline formations in the gallbladder. Symptoms include pain and most are treated through cholecystectomy to remove the gallbladder.
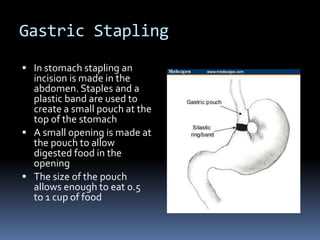
Gastric stapling surgically reduces the size of the stomach to help with weight loss, but risks include infection and nutritional deficiencies. Success rates are low.
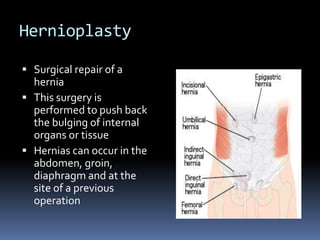
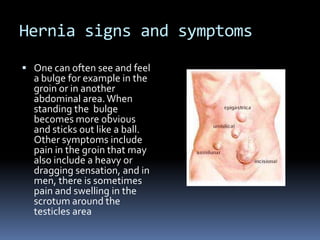
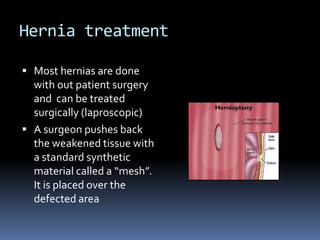
Hernioplasty repairs hernias by surgically pushing bulging tissue back with mesh. Complications can include rejection of mesh material