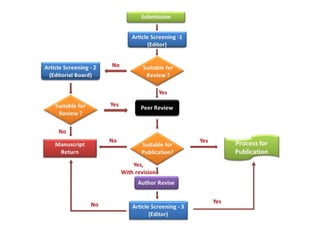
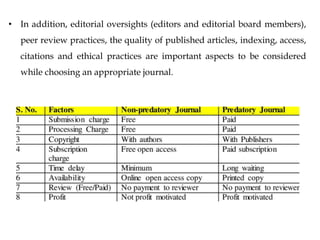
This document provides guidance on preparing and publishing a scientific manuscript. It discusses important steps like choosing an appropriate journal, writing each section of the manuscript such as the introduction, materials and methods, and results. Key details that should be included in each section are outlined, such as stating the study aims clearly in the introduction and providing enough methodological details to allow other researchers to replicate the study. Following guidelines for reporting clinical trials, observational studies, and systematic reviews can improve manuscript clarity and completeness. The overall goal is to help researchers overcome barriers and successfully publish their work.