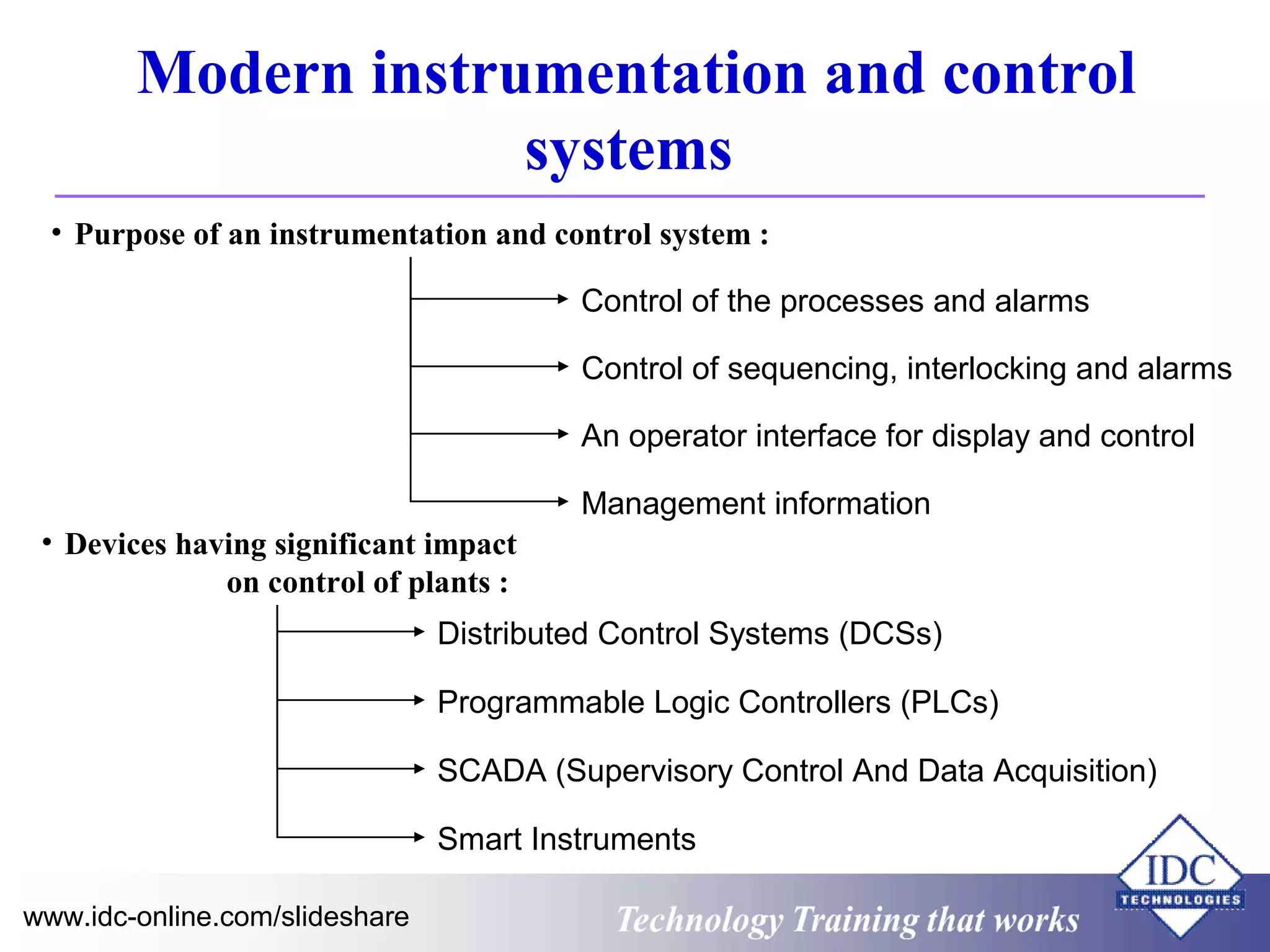
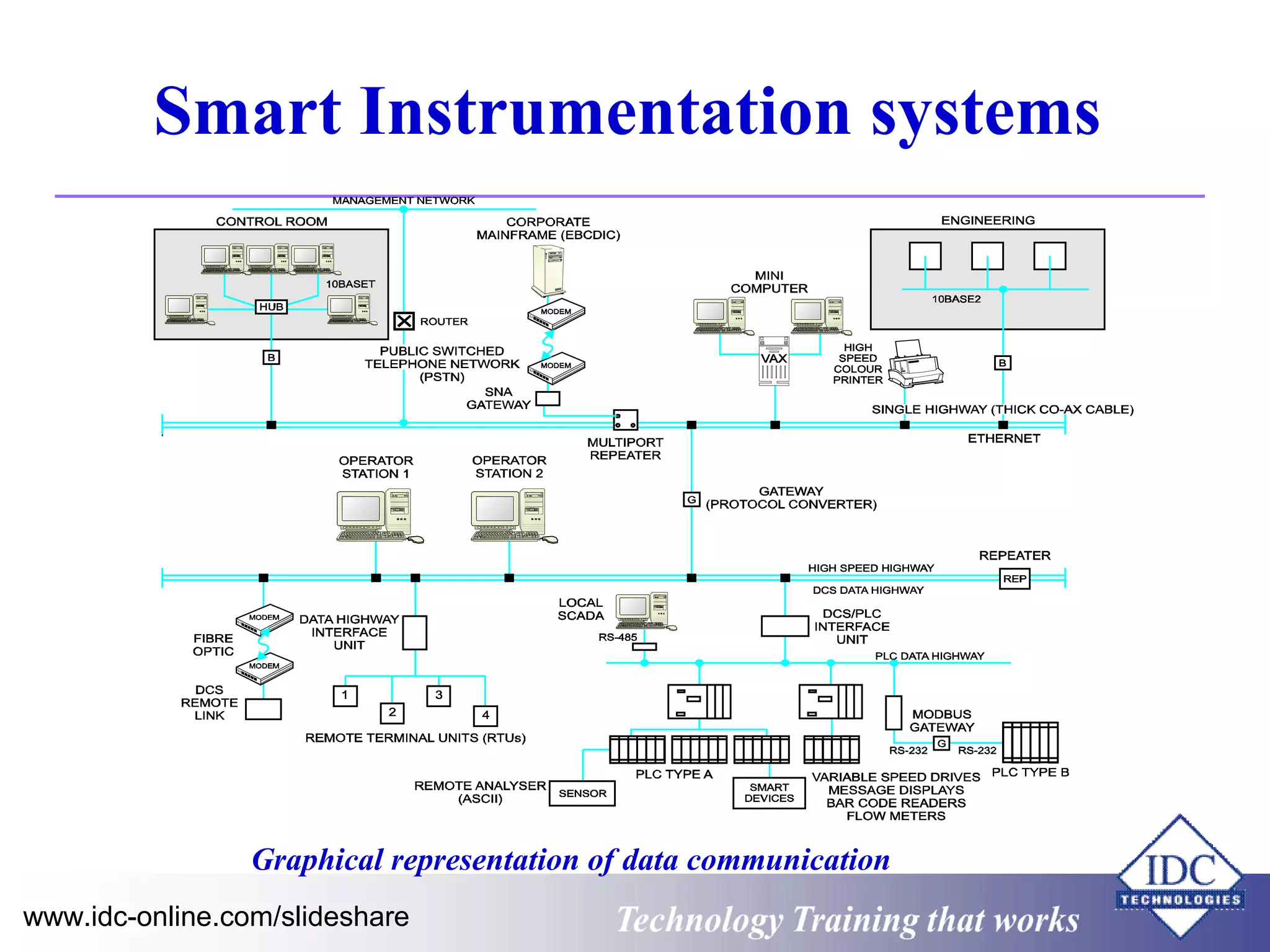
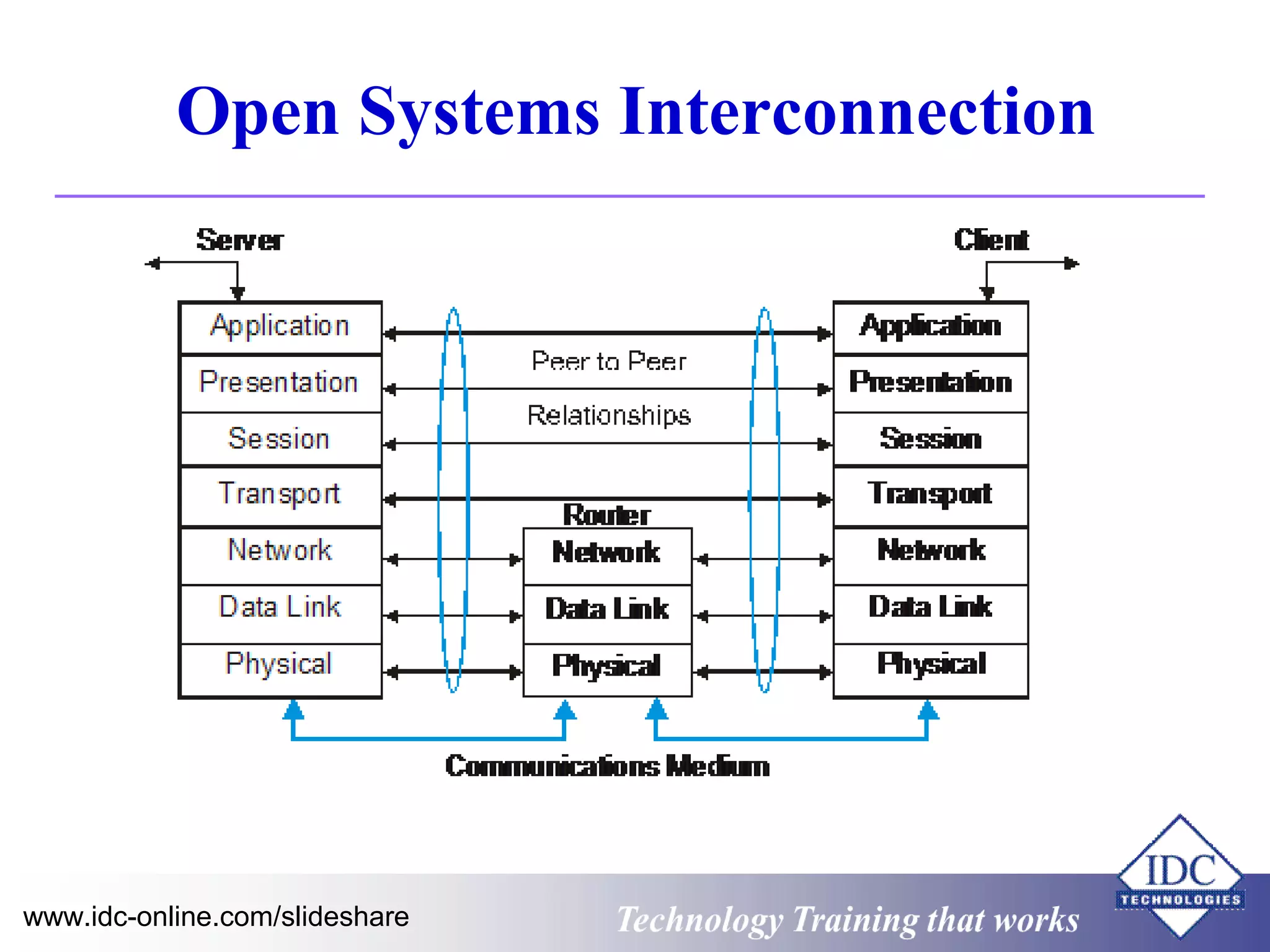
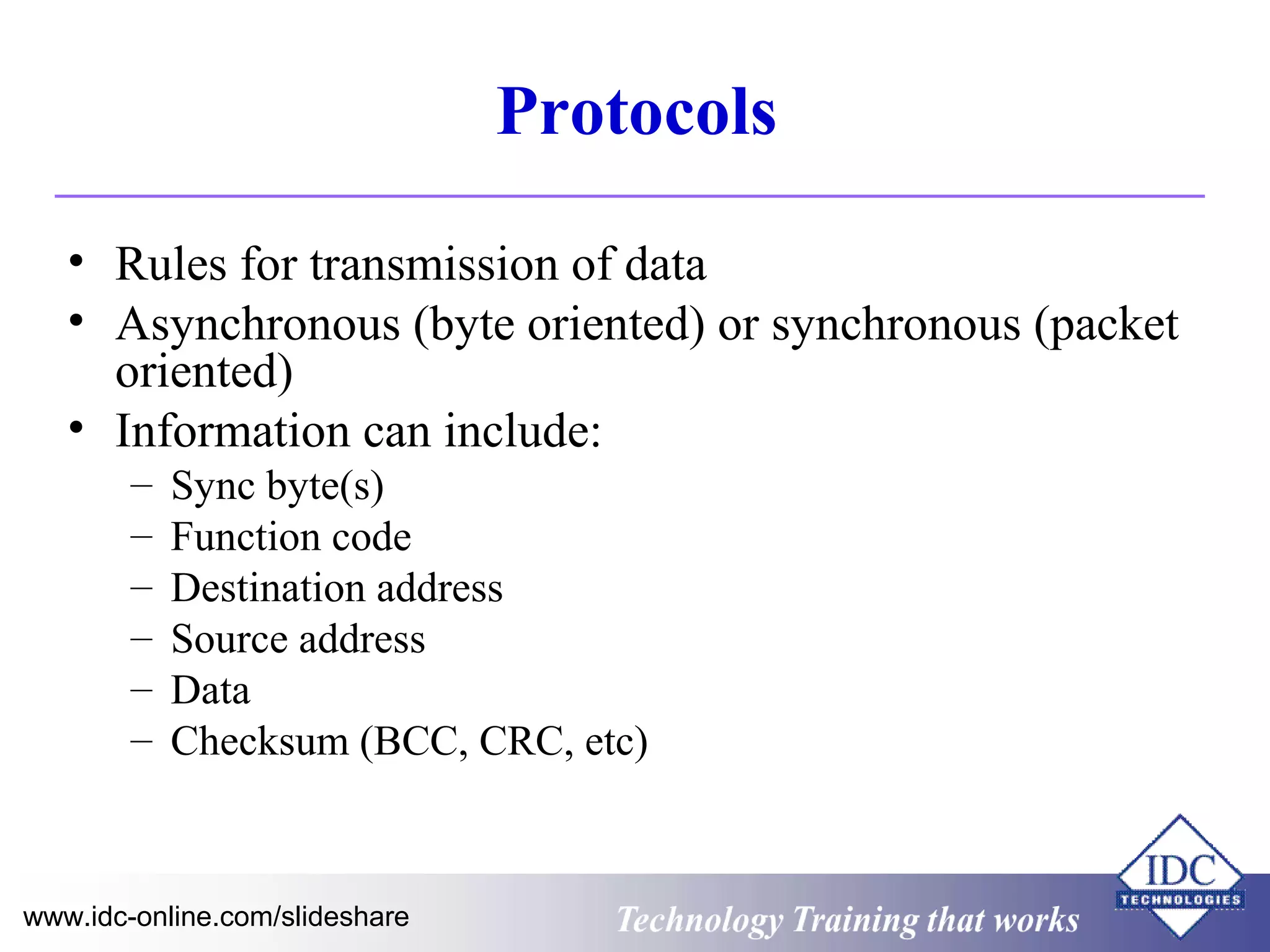
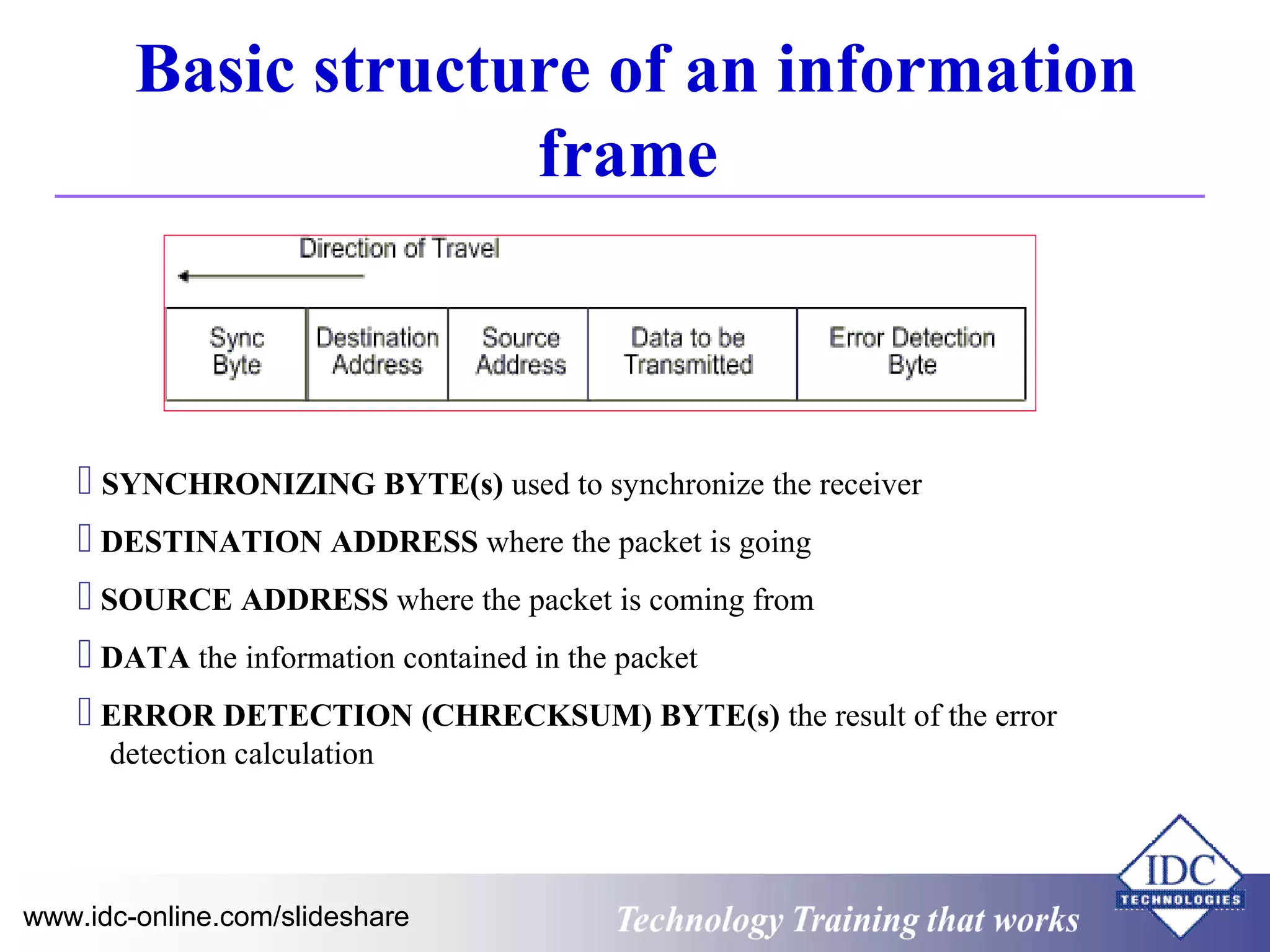
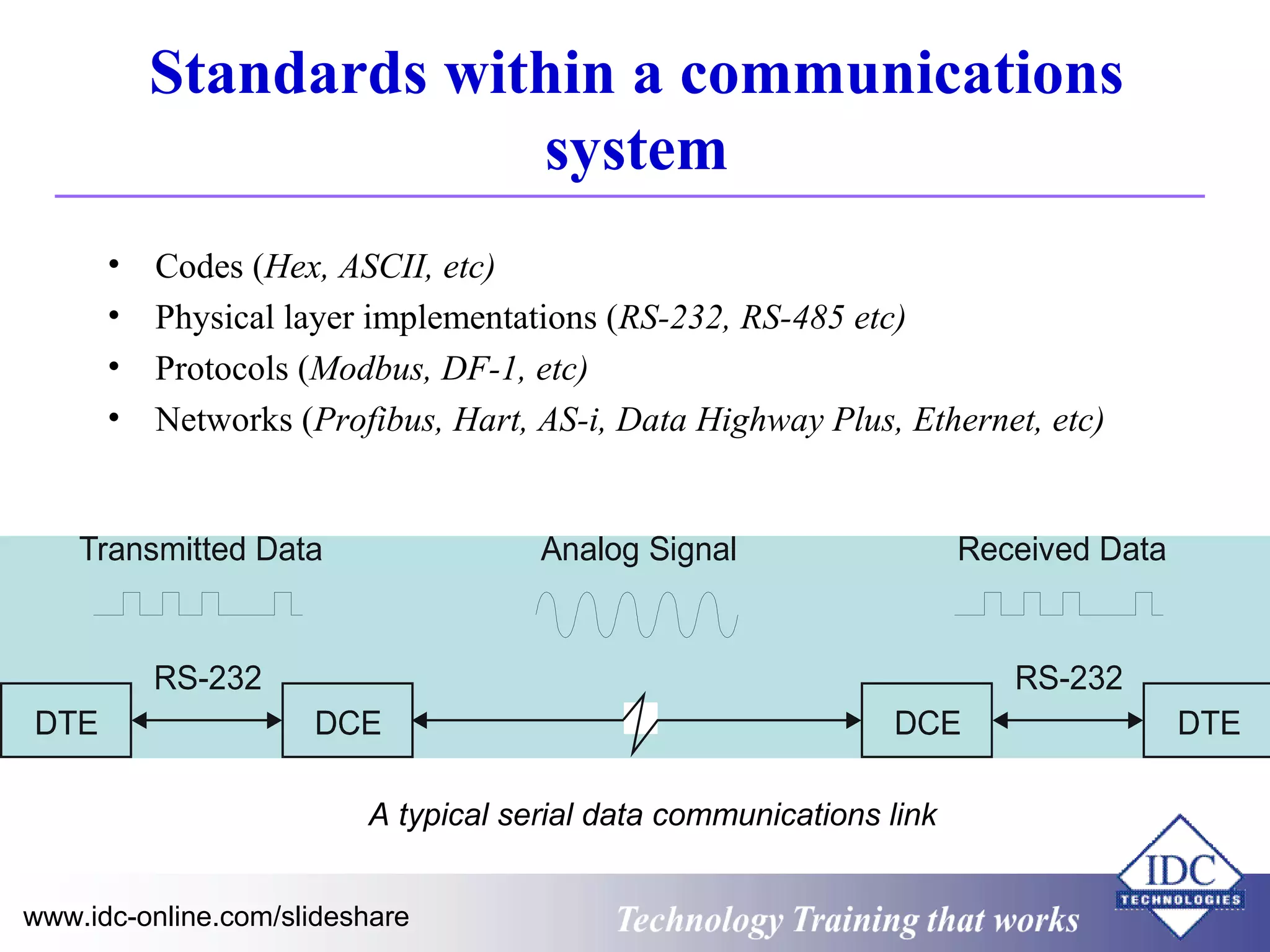
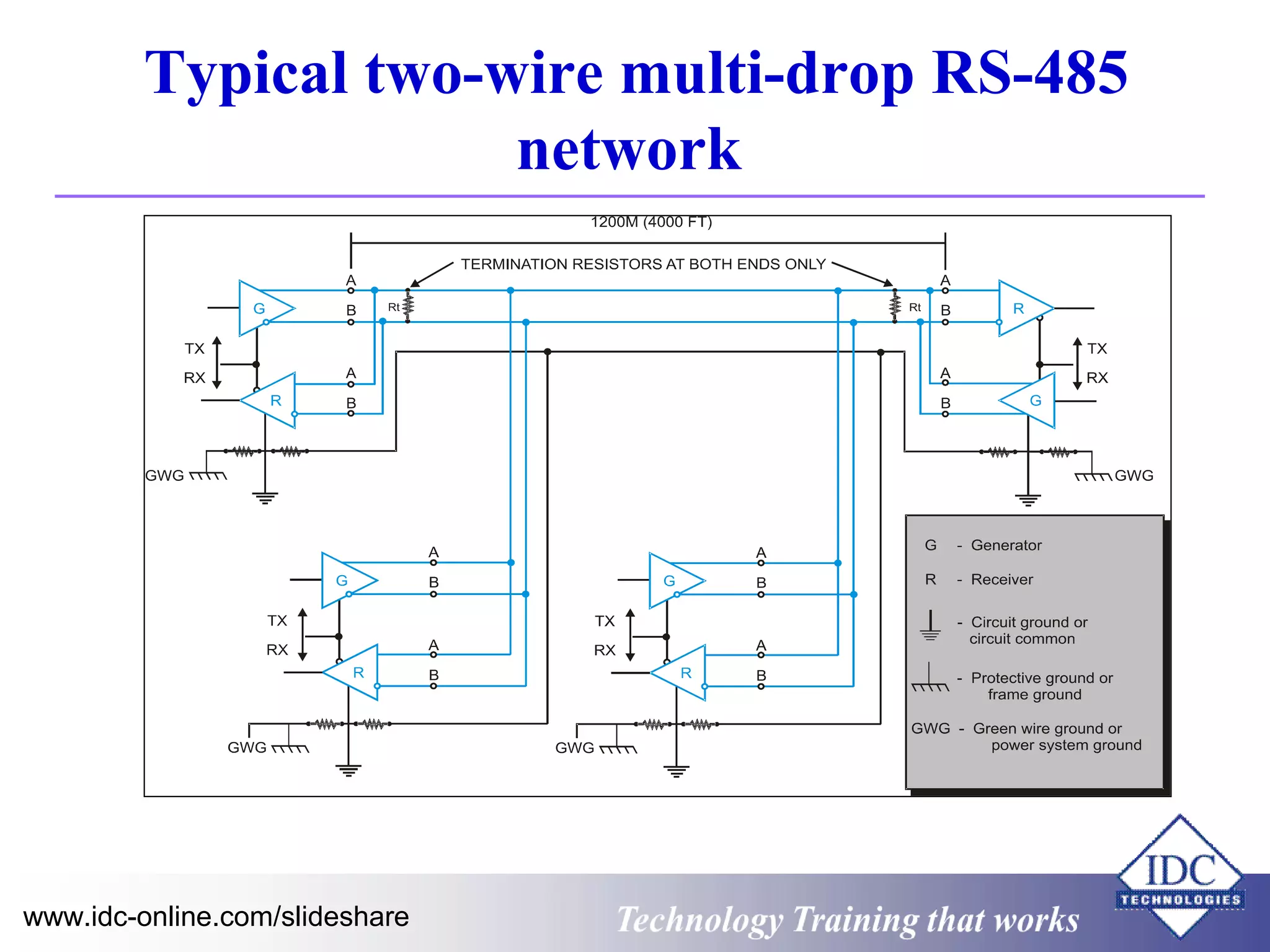
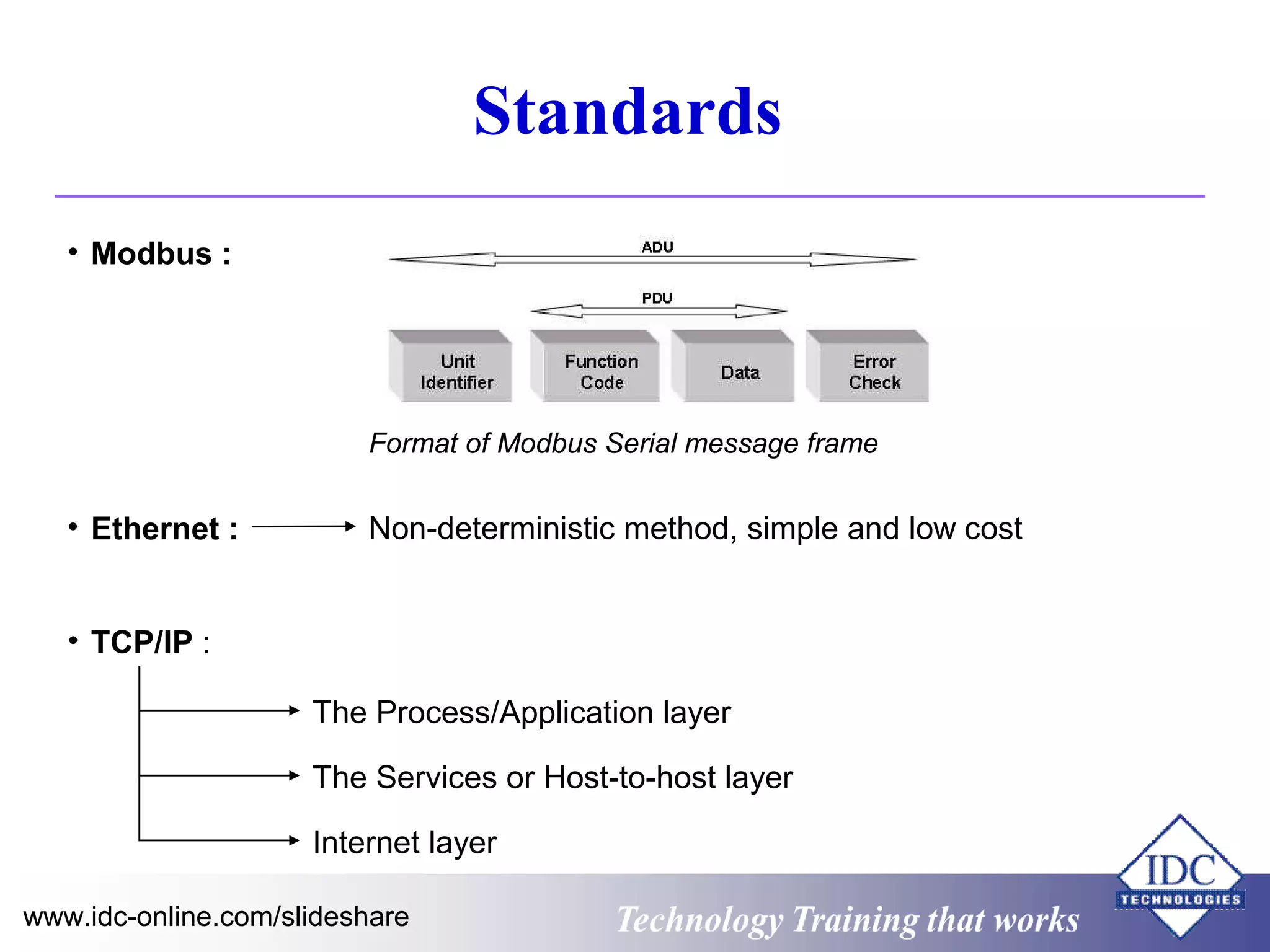
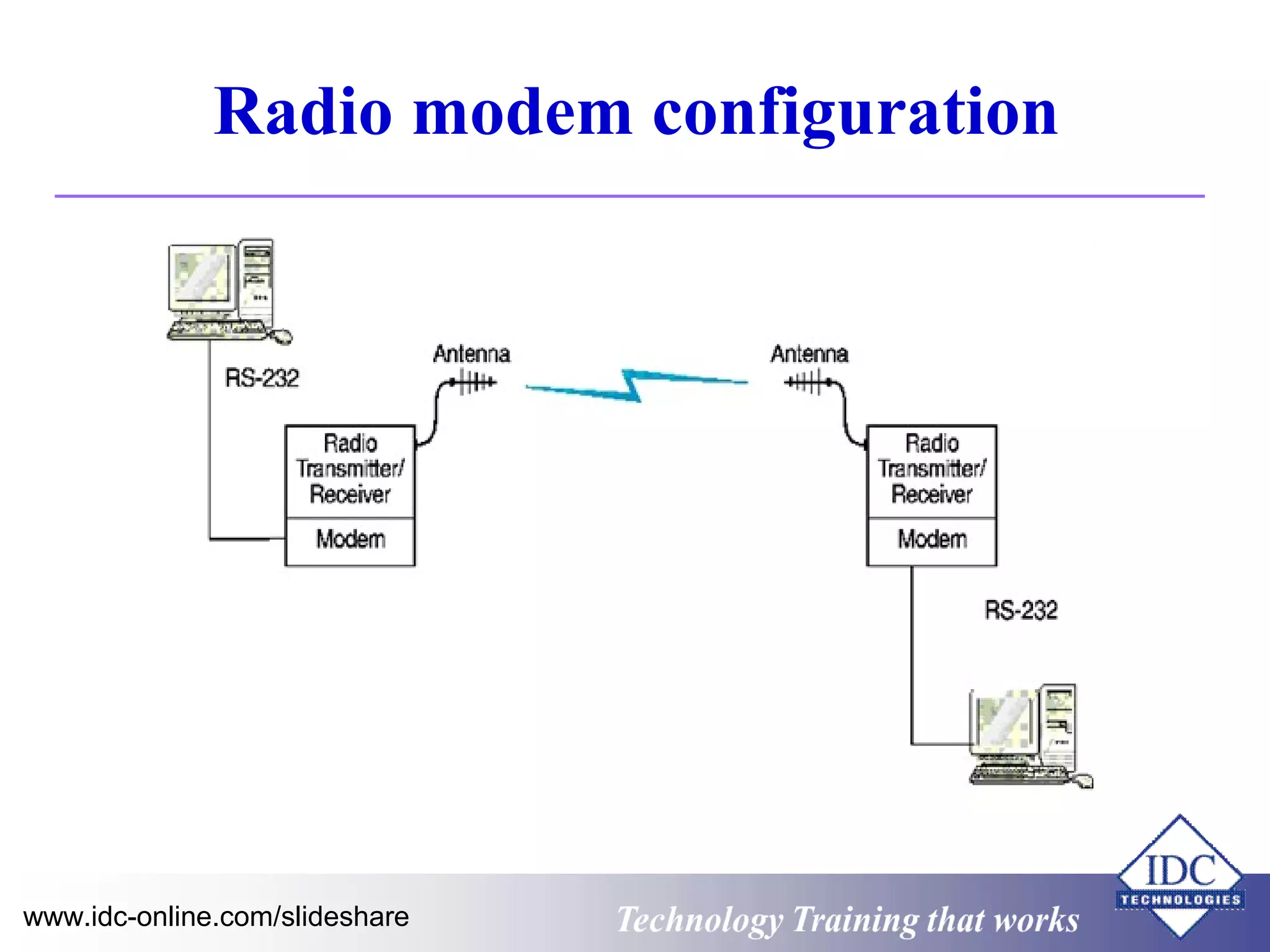
The document outlines technology training focused on troubleshooting and problem-solving of Modbus protocols within modern instrumentation and control systems. It includes descriptions of key components, communication protocols, and standards that govern industrial communication systems. Additionally, it provides an overview of the OSI model and various network standards relevant to data communications.