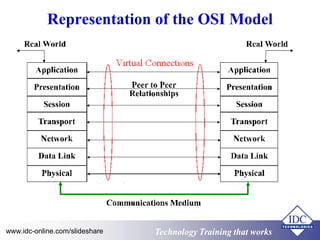
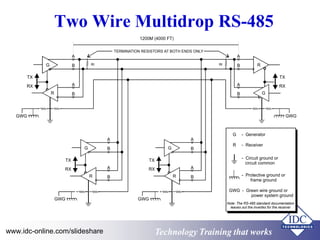
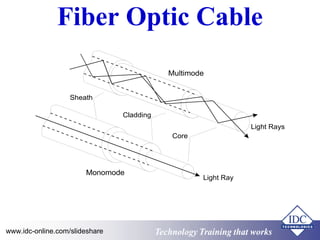
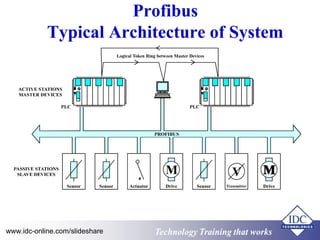
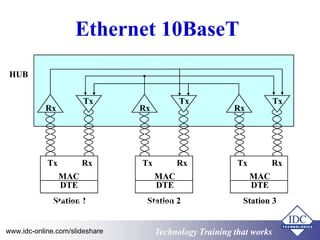
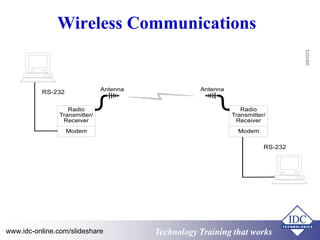
The document provides an overview of industrial data communications technology, covering essential topics such as the OSI model, SCADA systems, and various communication protocols like RS-485 and TCP/IP. It discusses the importance of information transfer, the structure of data frames, and modern solutions such as fiber optics and fieldbus architectures. Additionally, it mentions training opportunities for those seeking further information in this field.