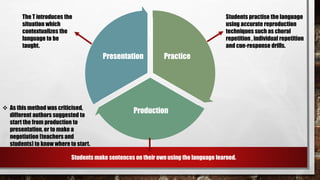
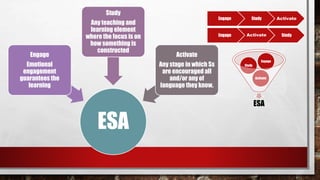
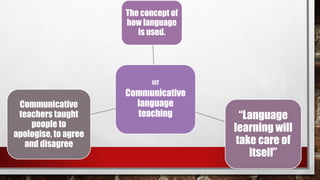
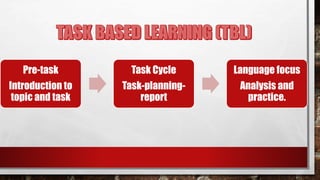
Approach refers to theories of language learning, method is the practical application of an approach using techniques and procedures. Techniques are specific classroom strategies while procedures are ordered sequences of techniques. Common historical approaches include grammar-translation which focused on grammar rules and sentence translation, the direct method which used only the target language, and audiolingualism which used repetition for habit formation. Later approaches include communicative language teaching focusing on language use, the lexical approach emphasizing vocabulary chunks, and student-centered dialogic methods.