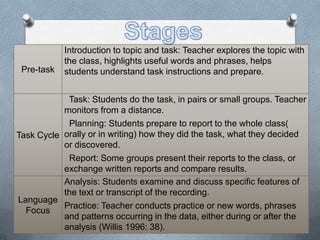
TBLL focuses on using authentic language tasks to promote meaningful communication. It uses real-world tasks to encourage interaction and language learning through purposeful engagement rather than isolated practice. Errors are seen as natural parts of the learning process as a learner's interlanguage develops over time. TBLL lessons follow a task cycle of preparation, task completion in groups, planning a report, and analysis to focus on language.