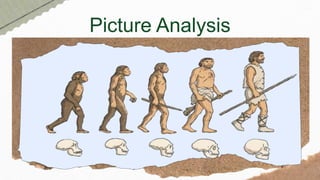
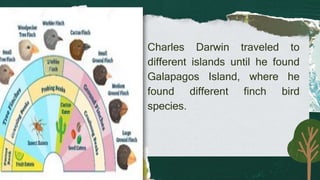
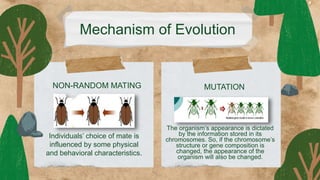
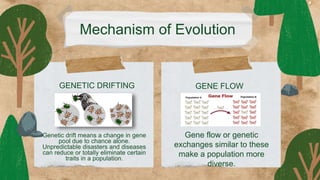
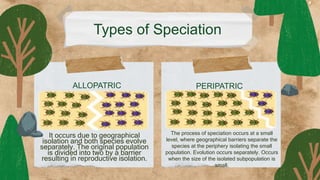
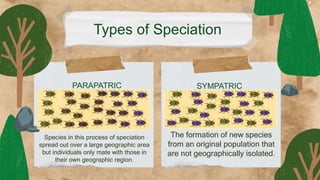
This document provides an overview of key concepts in evolution science. It discusses Jean Baptiste de Lamarck as the first evolutionist and his three theories of evolution: need, use and disuse, and acquired characteristics. It also covers Charles Darwin's theory of natural selection and how it led to the evolution of giraffes' long necks. The document then examines mechanisms of evolution like mutation, genetic drift, gene flow and natural selection. It defines speciation and the different types like allopatric, peripatric, parapatric and sympatric speciation. In the end, it provides a review questions and short test on these evolutionary concepts.