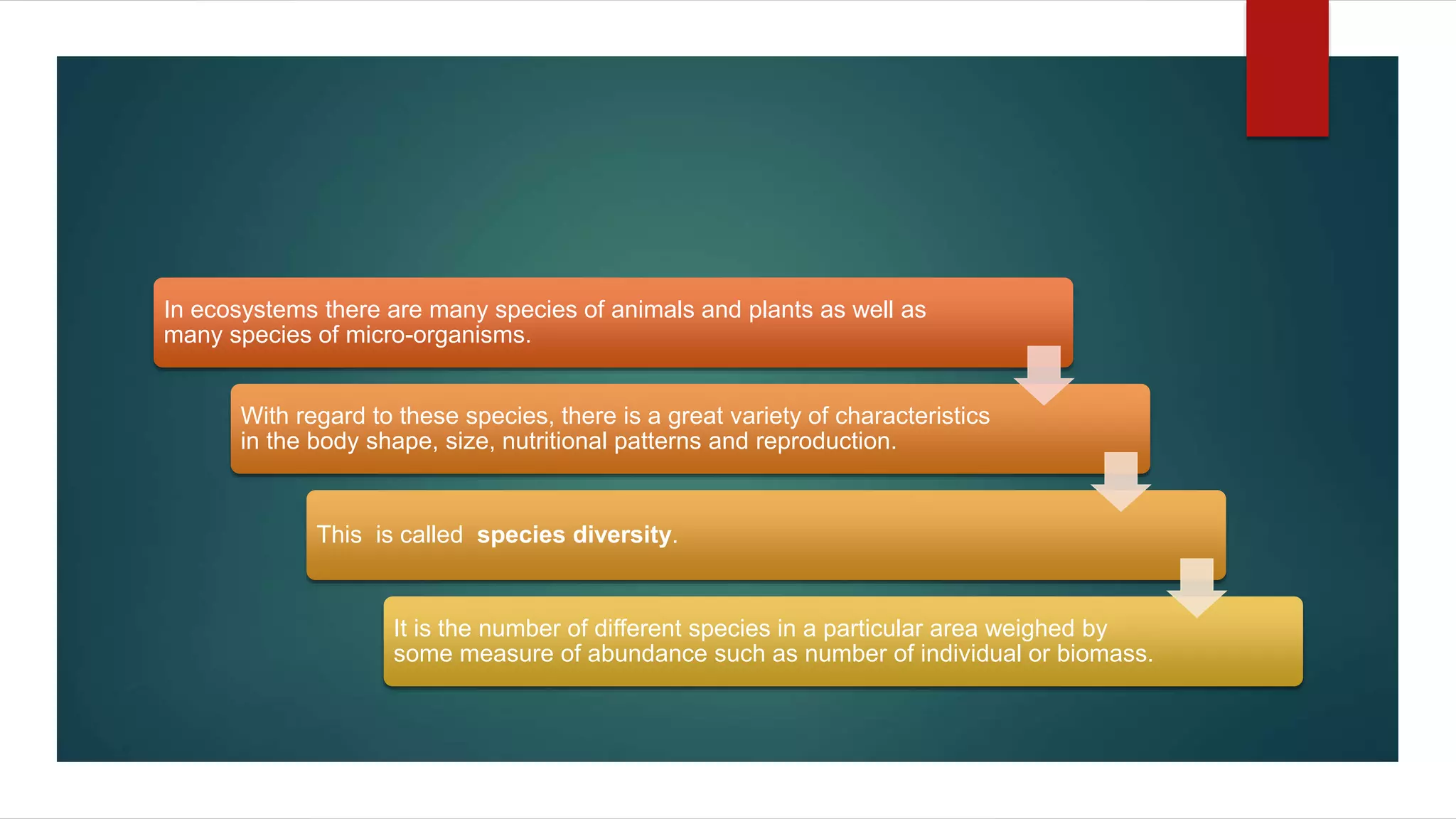
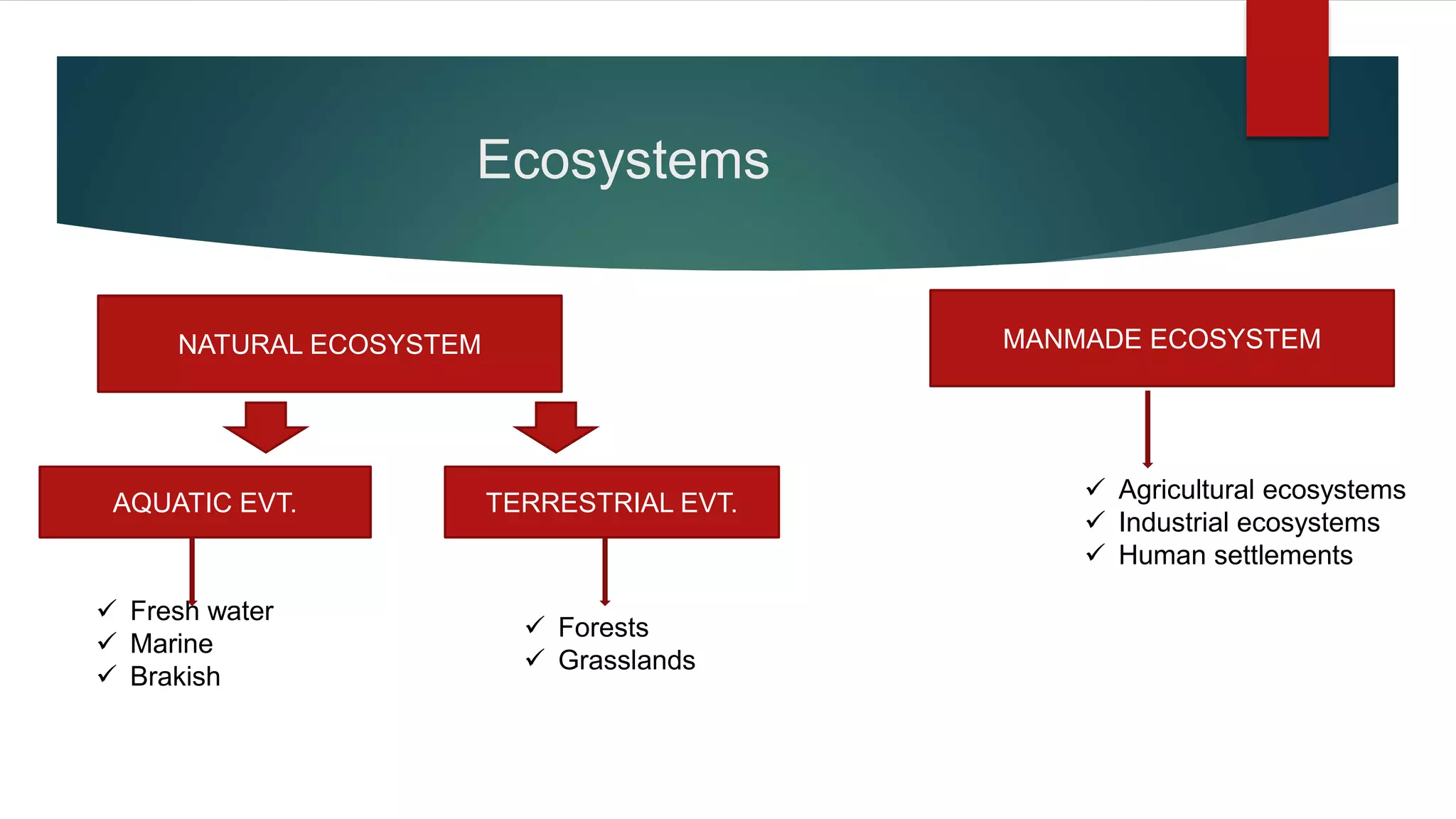
The document discusses biodiversity and ecosystems. It defines biodiversity as the variety of life on Earth, including diversity at the genetic, species, and ecosystem levels. Biodiversity is important as it increases ecosystem productivity and beauty, reduces competition between species, and provides resources for research, education, and entertainment. Threats to biodiversity include natural disasters as well as human activities like habitat destruction and pollution.