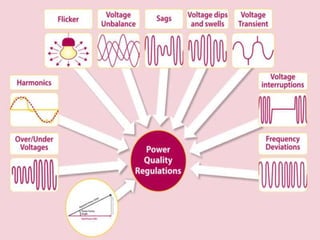
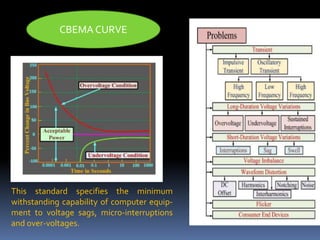
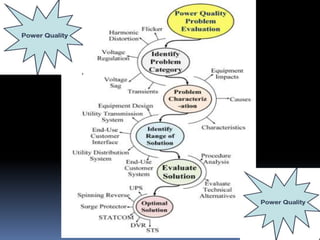
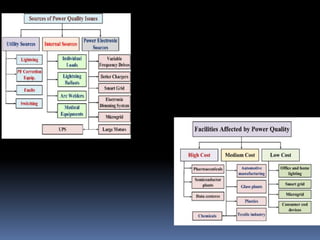
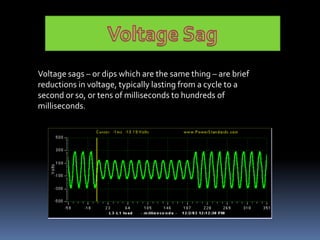
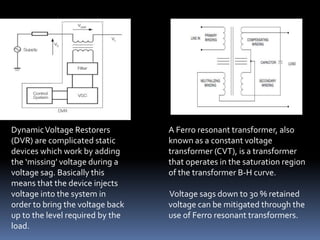
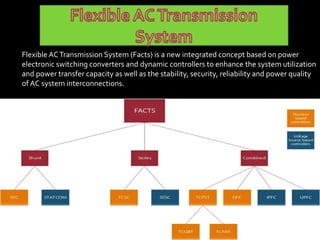
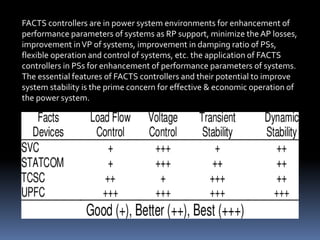
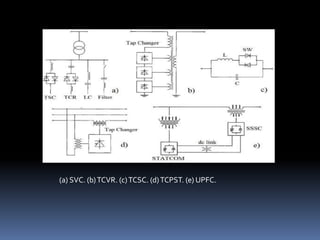
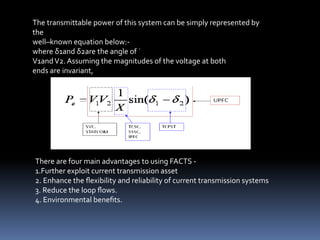
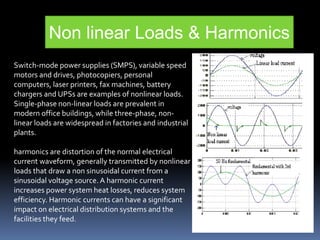
This document discusses power quality issues such as voltage sags, harmonics, transients, and facts controllers. It defines voltage sags as brief reductions in voltage lasting milliseconds caused by increases in current or system impedance. Harmonics are distortions of the normal waveform caused by non-linear loads. Transients are high magnitude disturbances under 50 milliseconds from sources like lightning or switching. FACTS controllers like SVC and UPFC use power electronics to enhance transmission system performance.