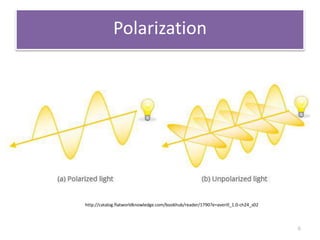
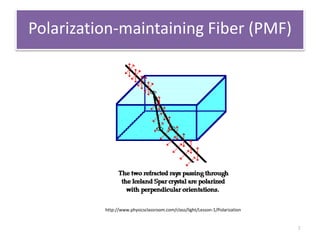
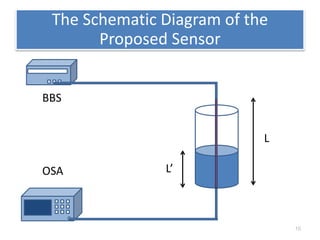
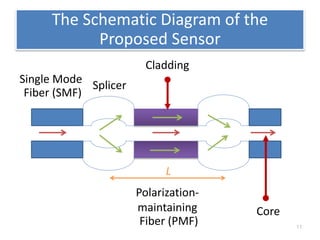
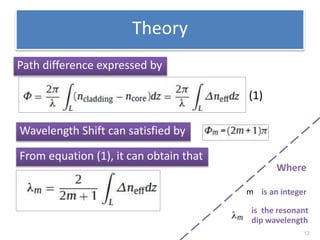
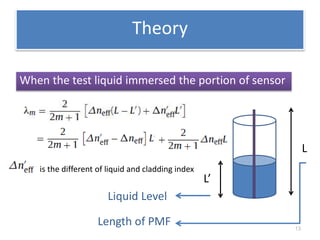
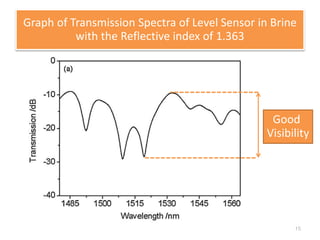
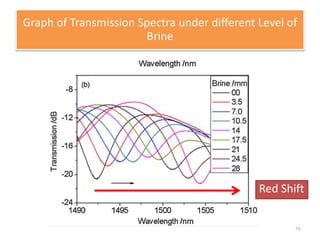
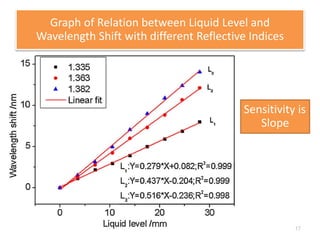
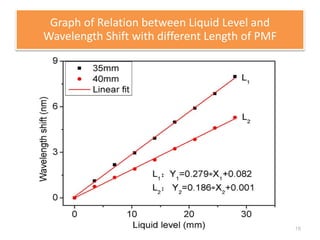
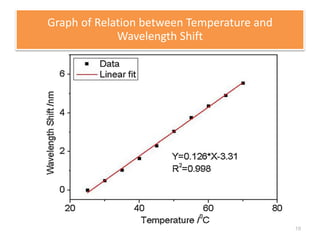
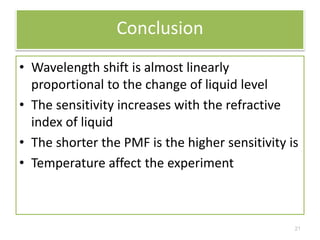
This document describes an optical liquid level sensor based on a polarization-maintaining fiber modal interferometer. The sensor uses a polarization-maintaining fiber spliced between two single-mode fibers to form an interferometer. Changes in the liquid level cause a change in the optical path difference, resulting in a wavelength shift that can be used to measure the liquid level. The sensor is easy to fabricate, structurally stable, and highly sensitive. Experimental results show that the wavelength shift increases linearly with liquid level and refractive index, and decreases with shorter fiber length and increasing temperature.