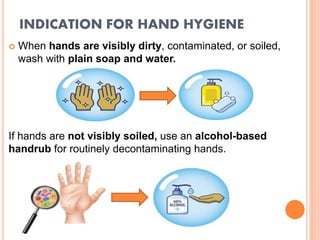
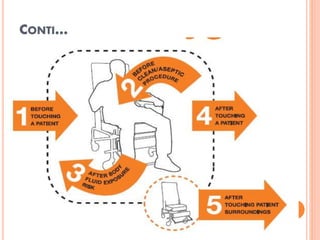
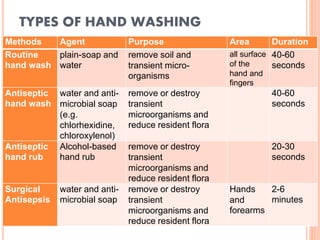
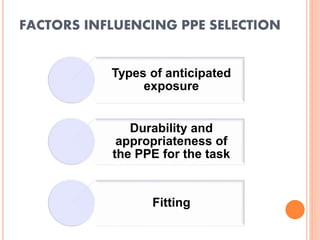
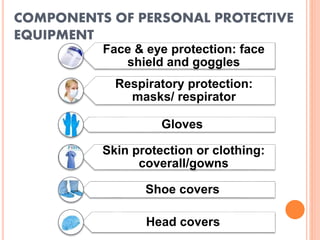
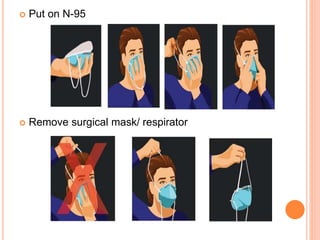
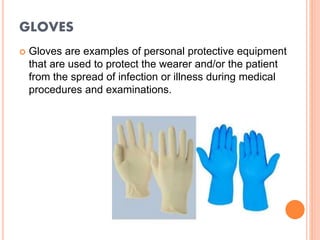
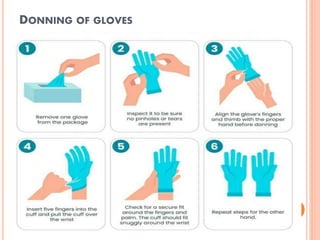
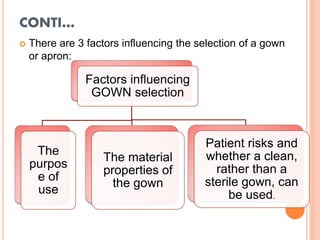
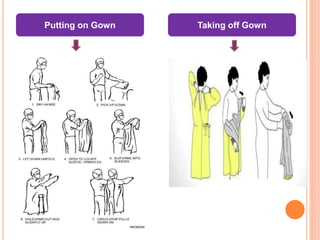
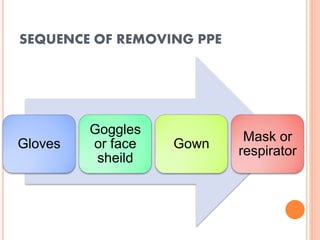
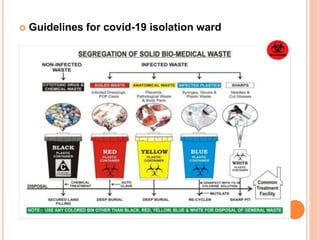
The document discusses personal protective equipment (PPE) used to prevent the spread of diseases like COVID-19. It defines standard safety measures and PPE, which includes face shields, gloves, gowns, masks, and shoe covers. The key steps for properly donning and doffing PPE like gowns and masks are outlined. Guidelines for disposing of used PPE from COVID-19 isolation wards according to biomedical waste rules are also provided.