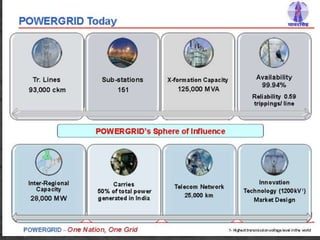
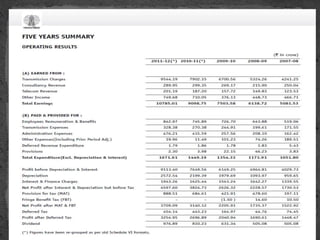
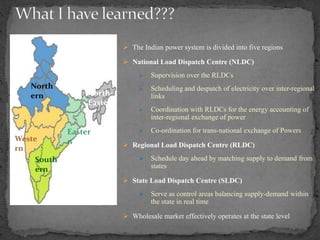
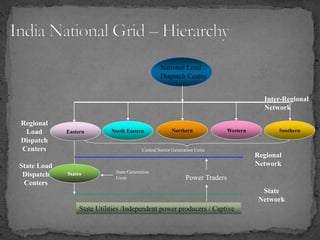
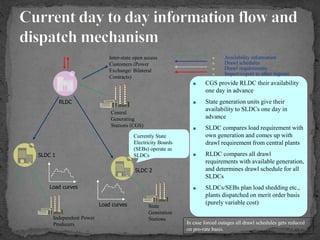
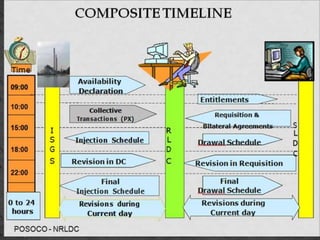
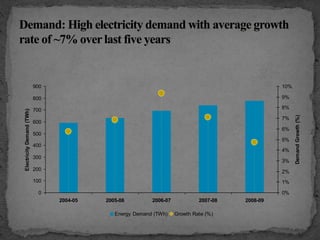
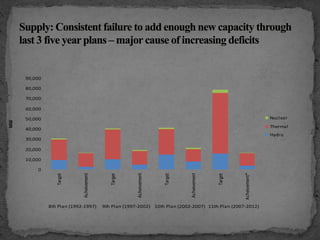
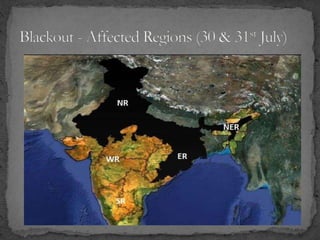
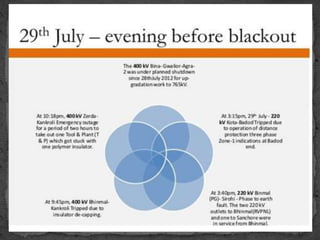
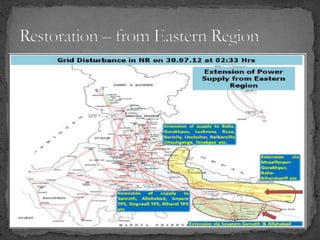
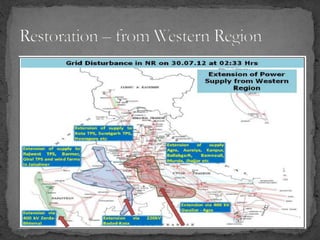
The document provides an overview of the Power System Operation Corporation Ltd (POSOCO), highlighting its responsibilities in managing and operating India's electricity grid through regional load dispatch centers (RLDCs) and the national load dispatch center (NLDC). It discusses the scheduling, dispatch of electricity, monitoring of system parameters, and coordination for energy accounting across regions. The document also touches on challenges such as grid collapses and demand forecasting issues, referencing significant incidents like the 2012 blackout impacting millions.