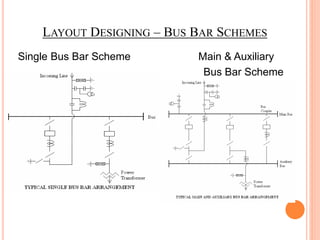
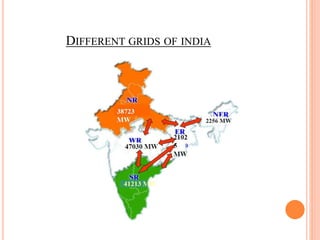
This document provides an overview of India's power grid operations. It describes the key components of the grid including interconnected power systems covering major territories called grids, and the benefits of interconnecting generating stations. It outlines the various equipment used in power grids like transformers and circuit breakers. The document also discusses the roles of central and state authorities in coordinating generation, transmission and distribution across states through load dispatch centers. It provides a brief history of developments of the power grid in India over time including integration of regional grids and use of higher voltage levels.