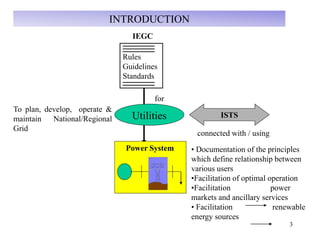
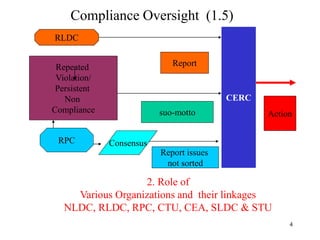
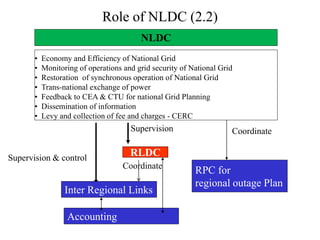
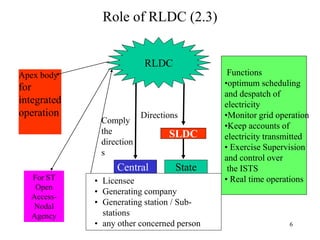
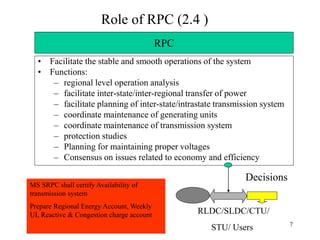
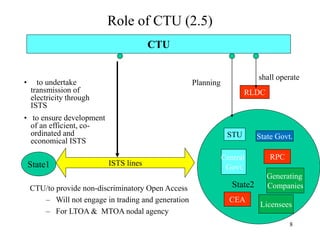
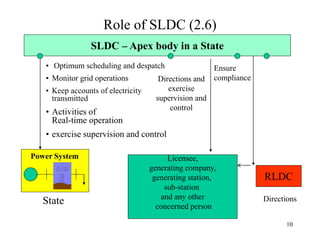
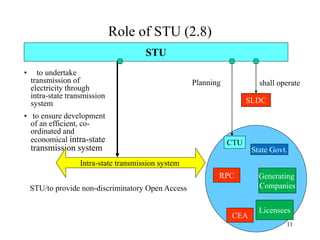
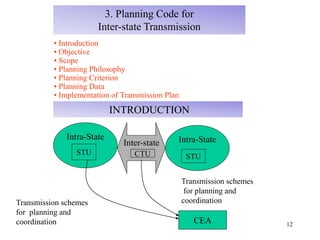
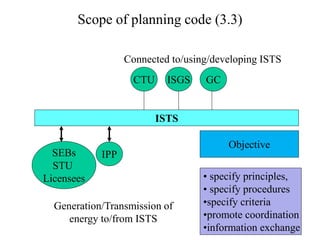
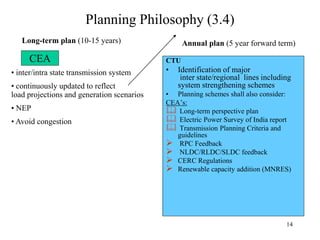
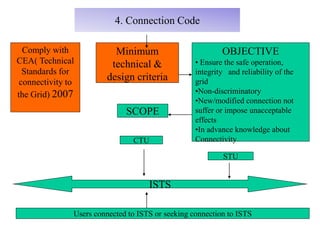
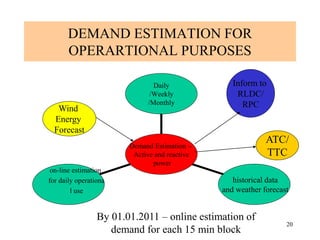
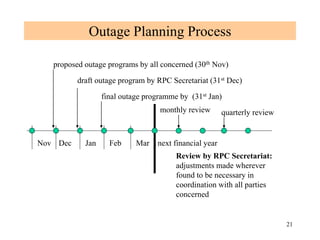
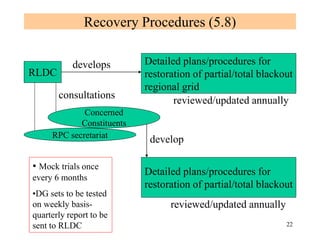
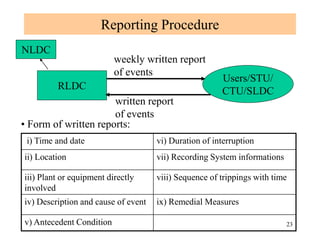
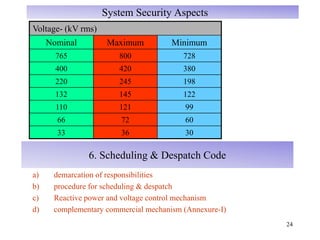
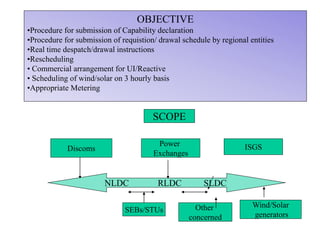
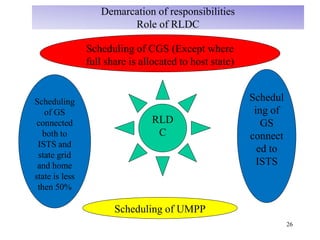
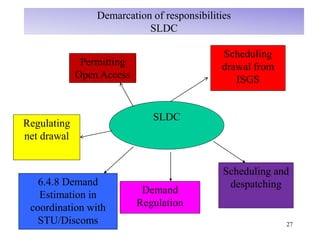
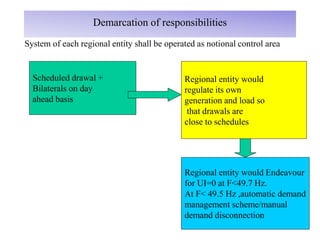
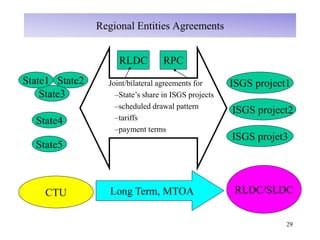
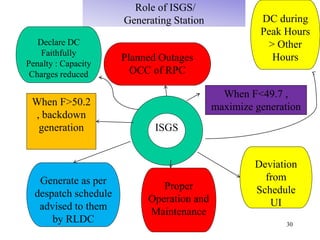
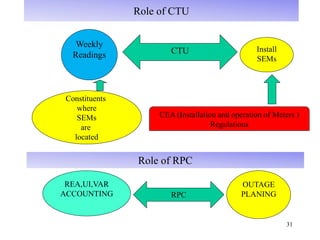
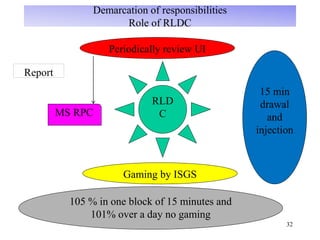
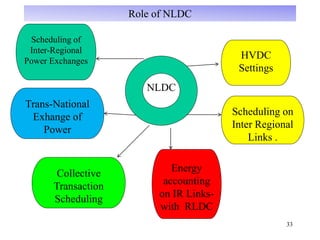
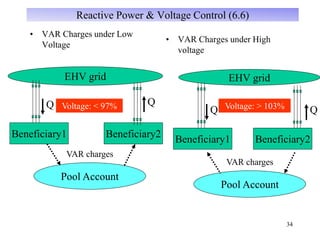
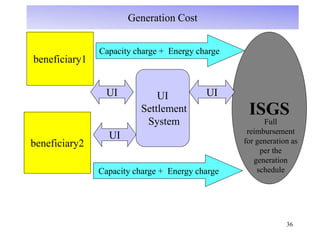
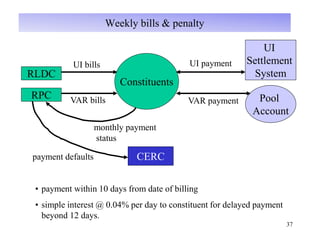
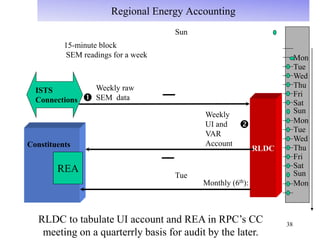
The document provides an overview of grid code technical recruitments in India. It discusses the roles of various organizations in electricity transmission planning and operations. The National Load Dispatch Center oversees national grid operations while Regional Load Dispatch Centers control regional operations. State Load Dispatch Centers control operations within states. Transmission utilities and state transmission utilities plan and develop inter-state and intra-state transmission systems respectively. The Central Electricity Authority issues technical standards and guidelines for transmission planning. Regional Power Committees facilitate coordination between states. The document also summarizes various codes related to transmission planning, grid connections, grid operations, and scheduling and dispatch of electricity.