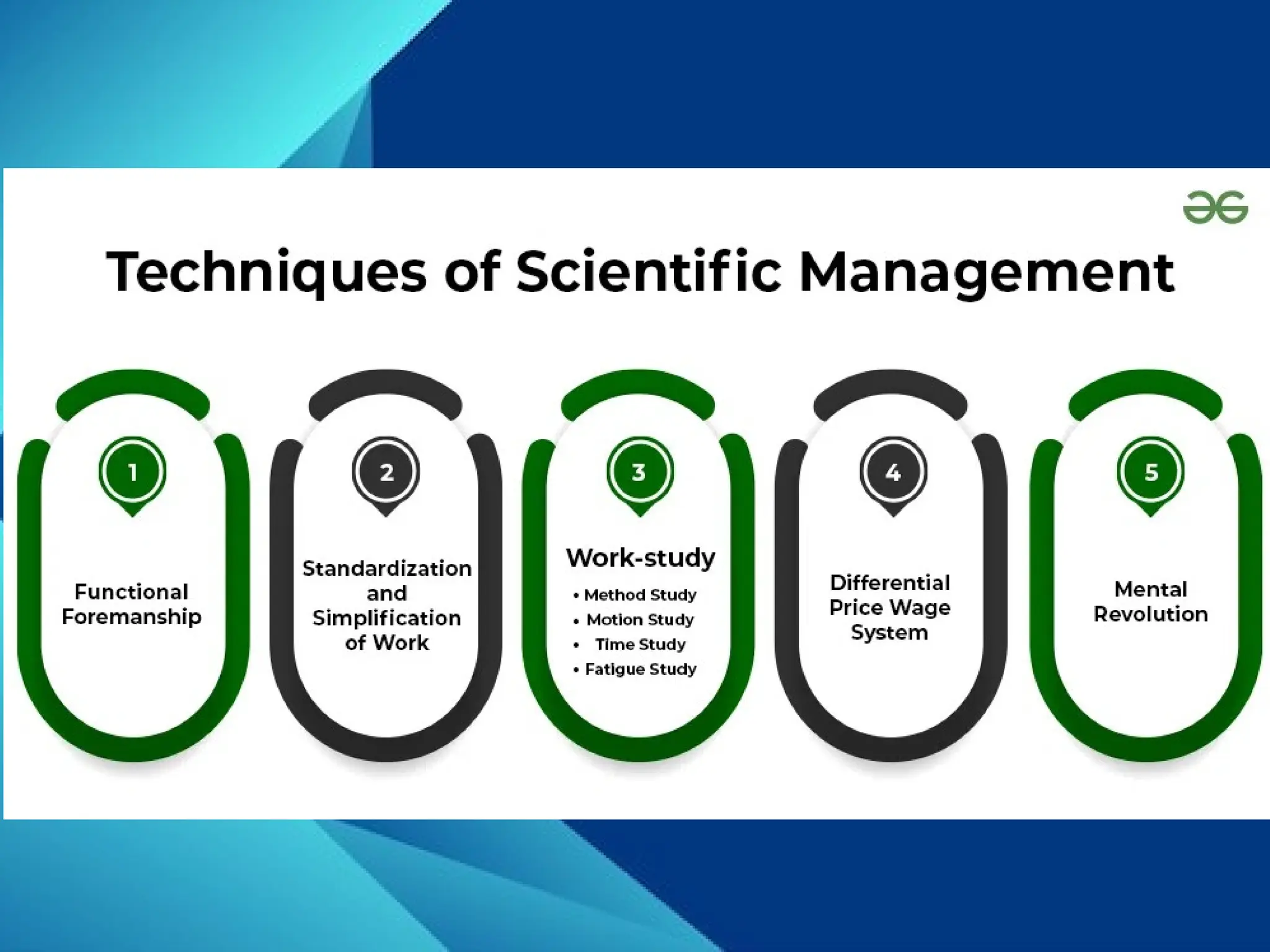
The document outlines the principles of scientific management, which aims to improve labor productivity and economic efficiency through techniques such as functional foremanship and work standardization. It details specialized roles for foremen to enhance supervision and describes methods including work, motion, and time studies to optimize tasks. The concept of a differential piece wage system incentivizes efficiency, while the 'mental revolution' promotes cooperation between management and workers, emphasizing the lasting relevance of these principles in modern industry.








![Time Study This technique involves meticulously
analyzing the time taken to perform a specific job,
breaking it down into its individual components.
The goal is to determine the standard time required
for an average worker with reasonable skills and
abilities to complete the task
Fatigue study focuses on understanding and
mitigating the physical and mental tiredness
experienced by workers during their tasks [2].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/techniquesofscientificmanagement-241004014802-9401cfbc/75/TECHNIQUES-OF-SCIENTIFIC-MANAGEMENT-pptx-10-2048.jpg)


