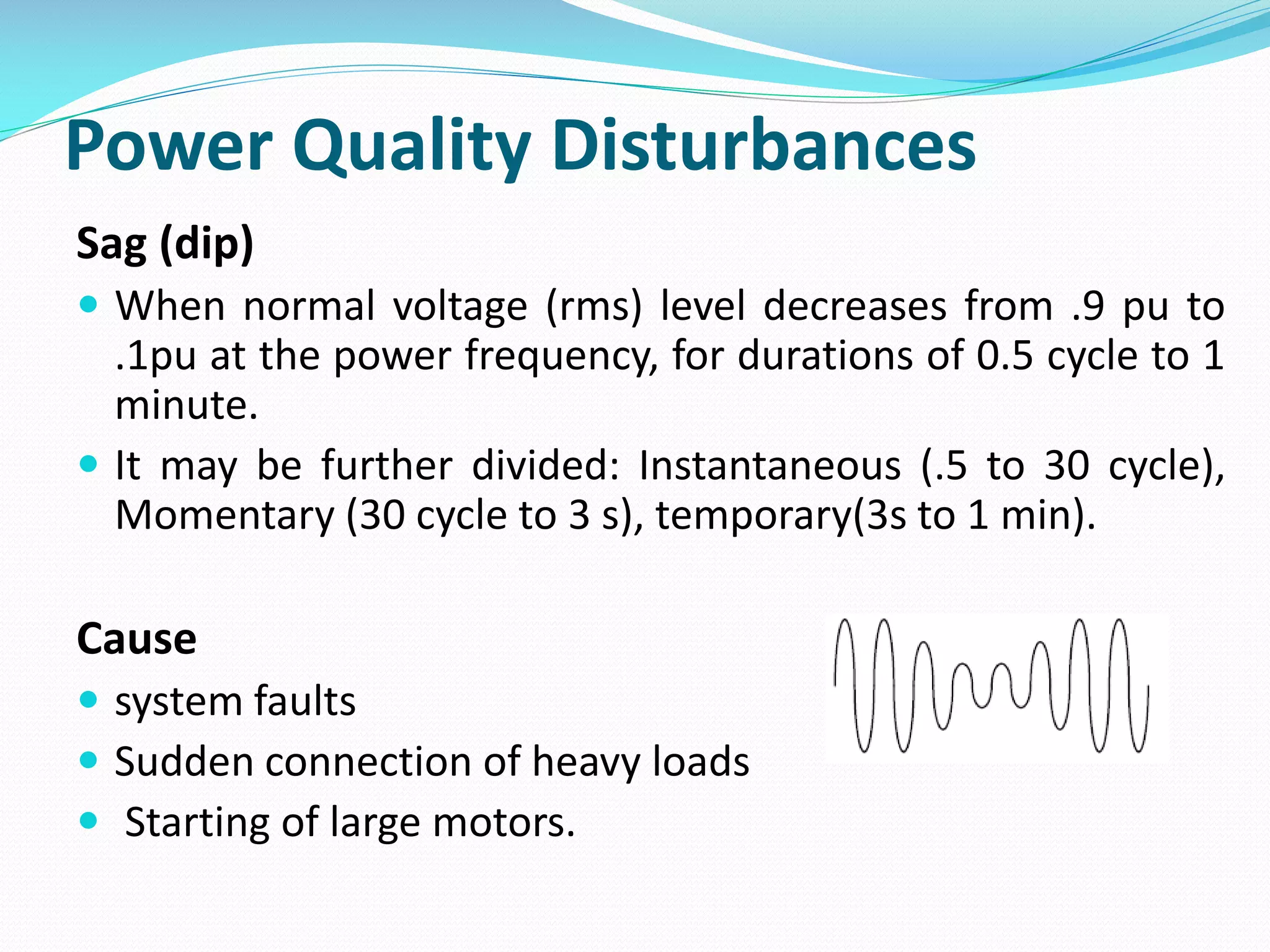
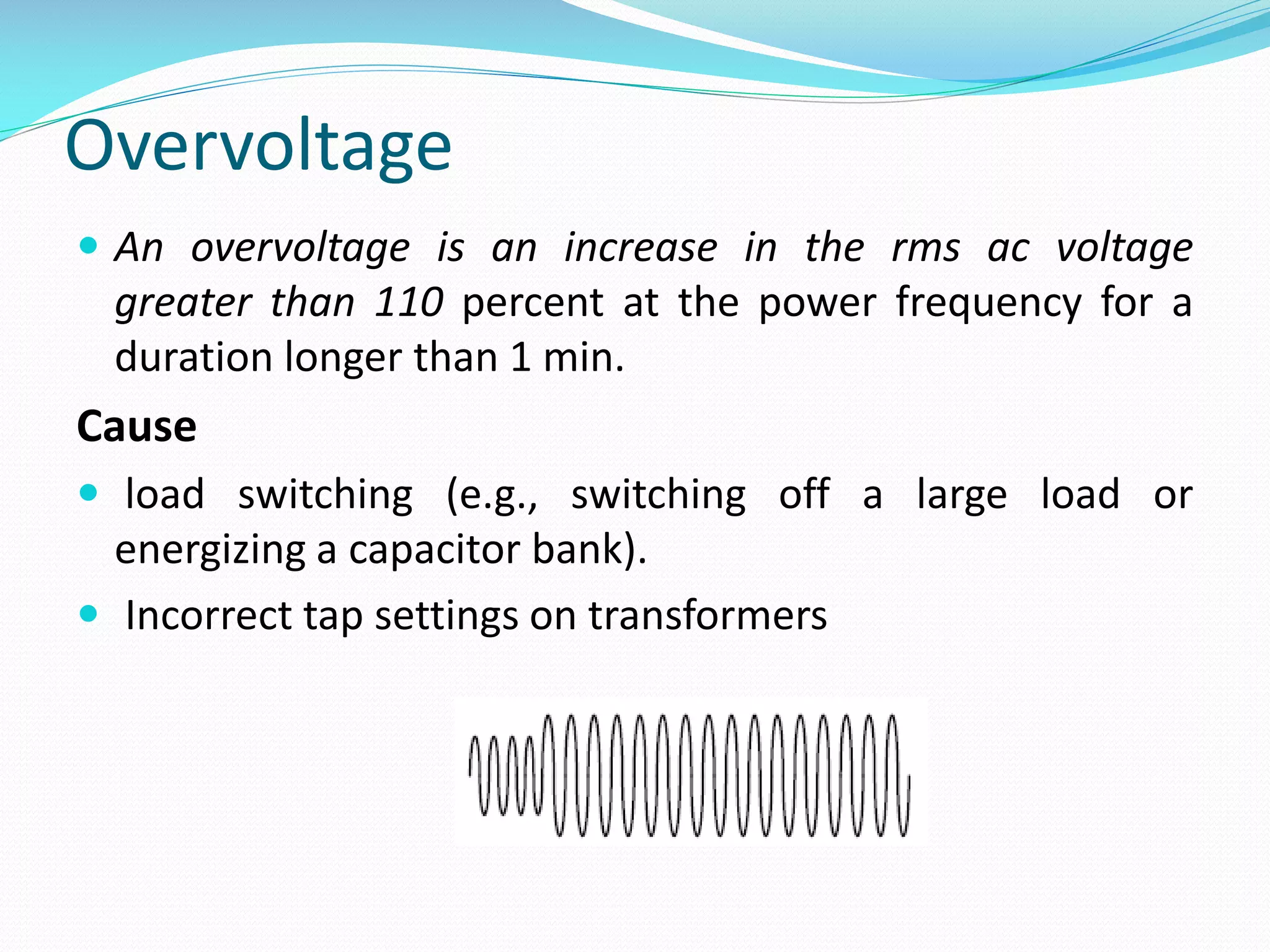
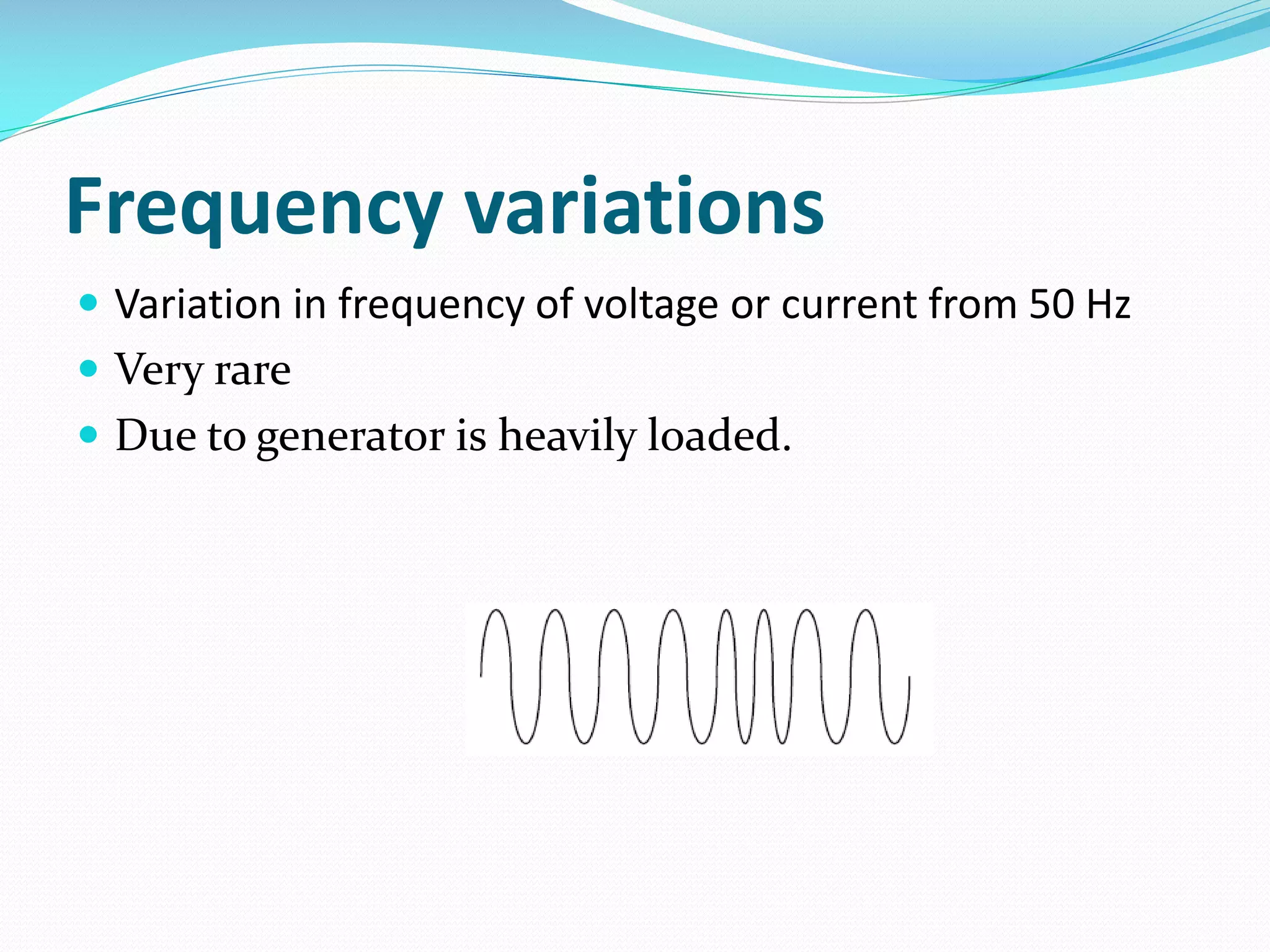
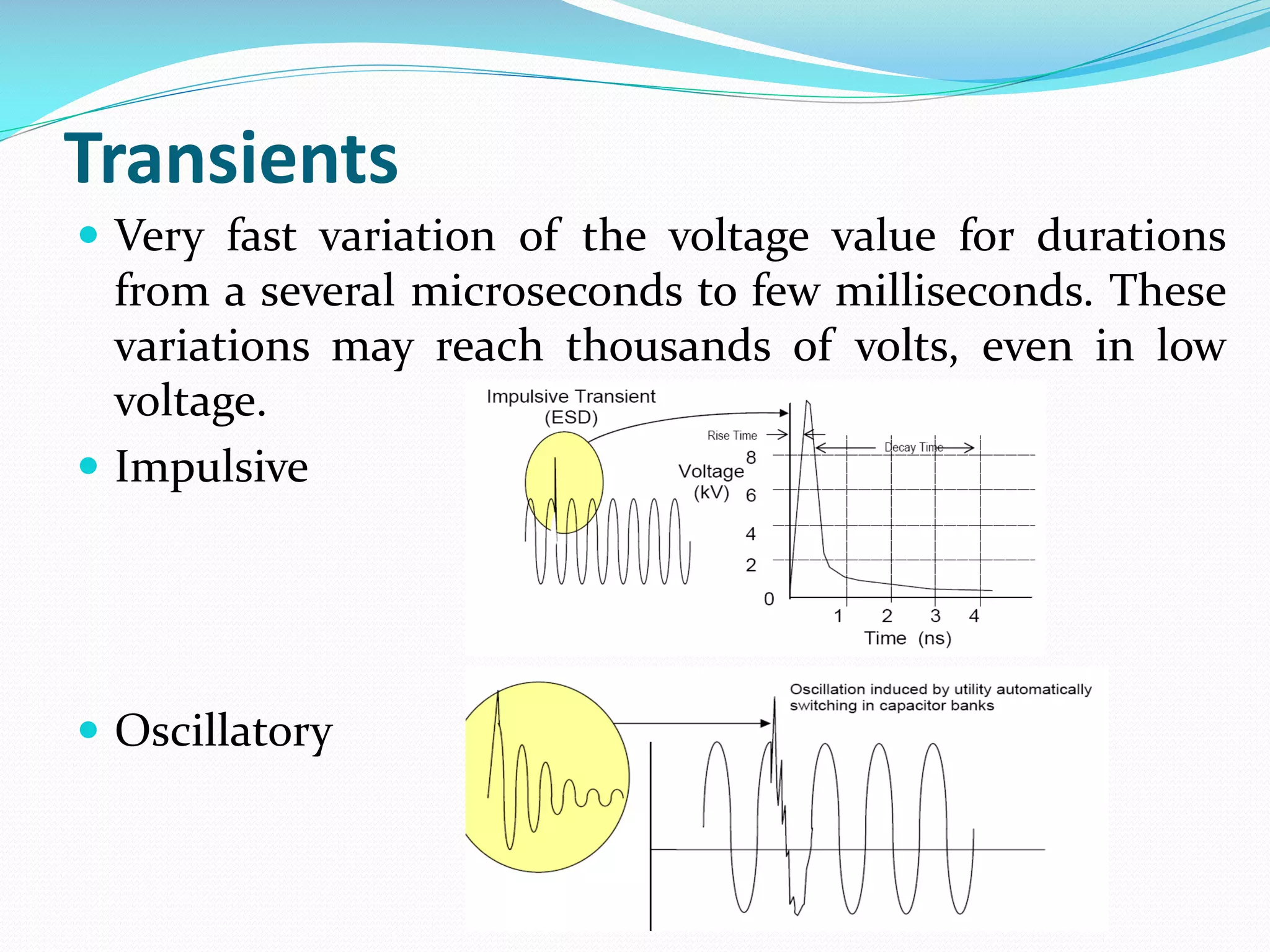
The document discusses power quality disturbances, defined as changes in voltage, current, or frequency that disrupt electrical equipment operation. It categorizes these disturbances into various types including sags, swells, overvoltage, and interruptions, explaining their causes and characteristics. The increasing reliance on automated devices has made power quality an important concern in electrical engineering.