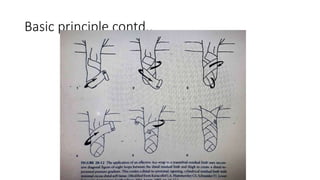
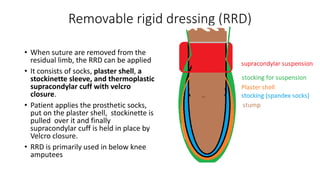
This document discusses various types of post-operative dressings for amputees, including their advantages and disadvantages. It describes soft dressings, semi-rigid dressings, removable semi-rigid dressings, rigid dressings without immediate post-operative prosthetics, and removable rigid dressings. Each dressing type provides different levels of edema control, wound protection, and residual limb shaping as the amputee progresses towards being fitted with a prosthetic. Choosing the appropriate dressing involves balancing factors like ease of application and inspection, circulation concerns, and preparing the residual limb for prosthetic use.