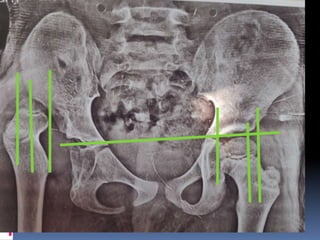
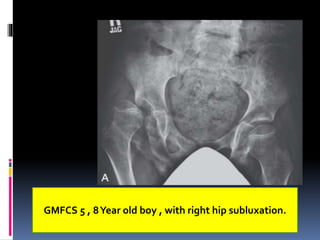
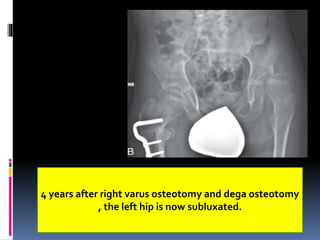
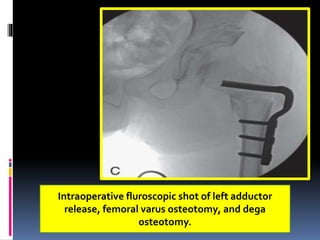
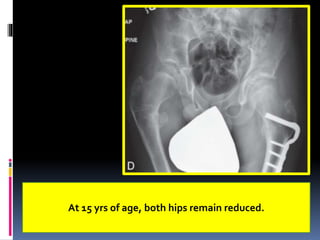
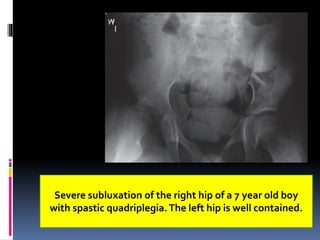
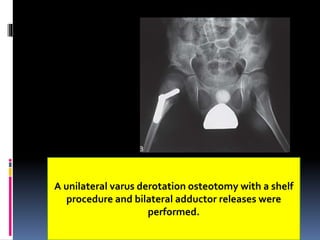
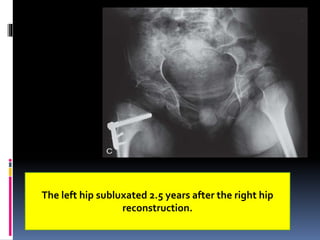
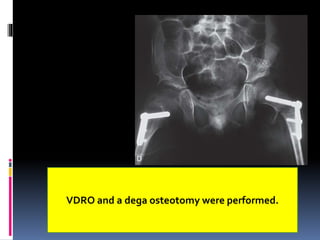
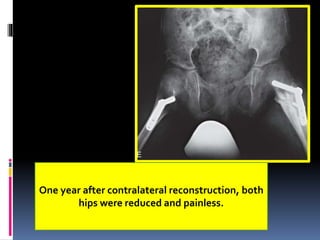
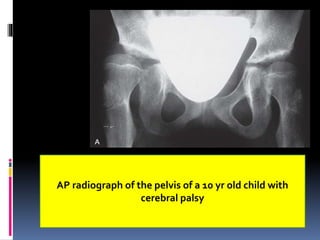
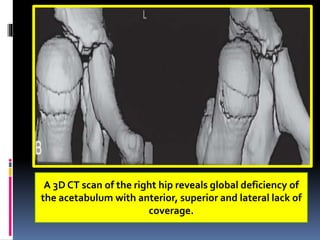
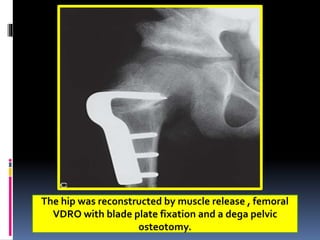
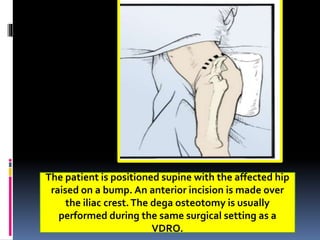
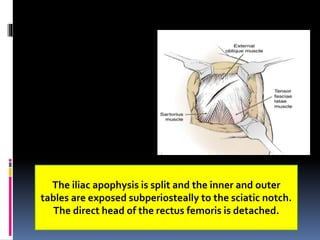
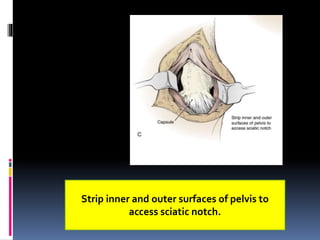
This document describes the surgical technique for performing a Dega pelvic osteotomy to treat hip subluxation in patients with cerebral palsy. Key steps include making an osteotomy through the outer table of the ilium from the anterior inferior iliac spine to the sciatic notch while leaving the inner table intact. Bone grafts are used to prop open the osteotomy and redirect coverage. Studies have found this procedure, combined with adductor and soft tissue releases and femoral osteotomies, can reduce subluxated hips in 95% of cases at 7 years follow up.