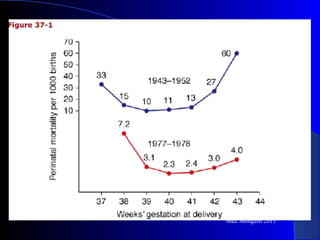
This document discusses post-term pregnancy, which is defined as pregnancy extending beyond 42 weeks from the last menstrual period. Risks to the fetus include doubling of perinatal mortality and risks to the mother include increased risk of labor abnormalities and cesarean delivery. The preferred course of management is induction of labor between 41-42 weeks, as this is supported by evidence of reduced perinatal mortality, morbidity and cesarean section rates. Membrane sweeping can also be used to prevent post-term pregnancy by reducing the percentage of patients going past term.