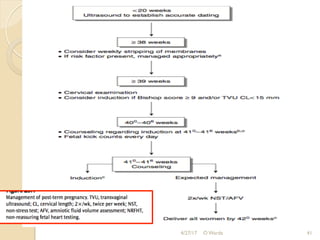
This document discusses post-term pregnancy, defined as a pregnancy extending beyond 42 weeks of gestation. It covers the epidemiology, etiology, risk factors, morbidity and mortality, diagnosis, and management of post-term pregnancies. The key points are:
1. The incidence of post-term pregnancy varies from 0.4-8.1% depending on location and methods of assessing gestational age. The causes are often unknown but may involve genetic or placental factors.
2. Risk factors include prior post-term pregnancy, nulliparity, advanced maternal age, obesity, male fetus, and inaccurate dating. Post-term pregnancies have higher risks of complications like macrosomia, dysmaturity syndrome