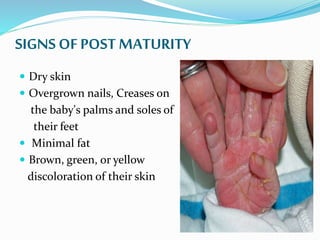
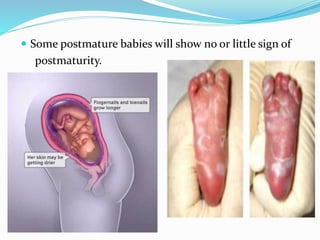
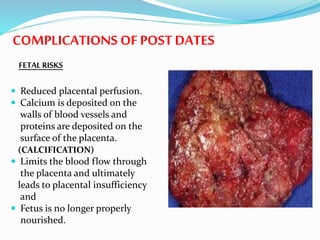
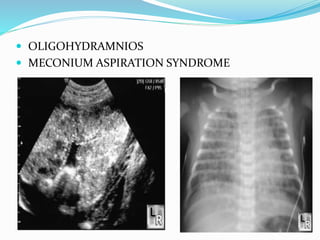
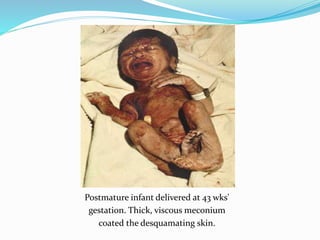
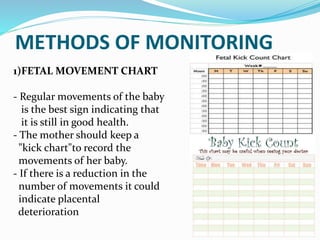
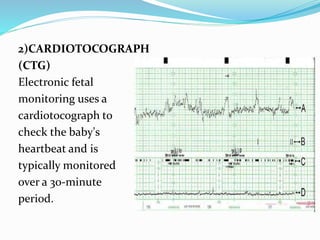
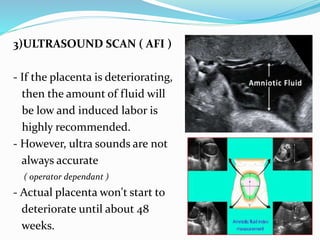
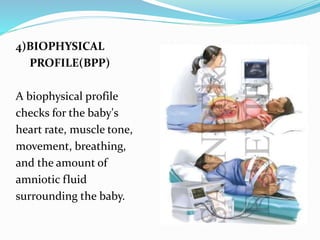
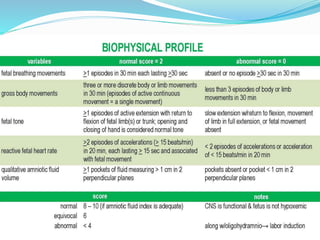
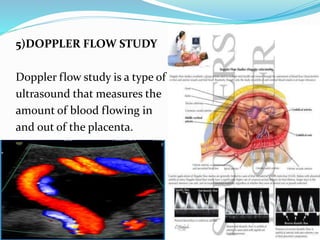
Post-term pregnancies are those that go beyond 42 weeks of gestation. The placenta starts to deteriorate after 42 weeks, limiting nutrients and oxygen to the fetus. This can cause complications like meconium aspiration and fetal distress. Monitoring options include fetal movement charts, CTG, ultrasound to check amniotic fluid levels and biophysical profiles. Labor induction is generally recommended over expectant management after 42 weeks to reduce risks.